Glutamine | What Does It Do And Should You Start Taking It?
📖 Table of Contents
Glutamine is a hot topic in fitness and wellness these days. From bodybuilders looking to speed up recovery to gut health enthusiasts seeking digestive relief, many people are curious about this supplement. But what exactly is glutamine, and what can it do for you? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what glutamine is, its key benefits (backed by science), who might need extra glutamine, how to use it effectively, and even how to choose a quality glutamine product. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of whether L-glutamine deserves a spot in your health and fitness regimen.
![]()
What Is Glutamine?
Glutamine is an amino acid, one of the 20 building blocks of protein in the body. It’s actually the most abundant amino acid in our bloodstream and muscle tissue. It is made up of the amino acids glutamic acid and ammonia, which combine to form L-glutamine. Your body can produce glutamine on its own, so it’s classified as a “conditionally nonessential” amino acid. Conditionally essential means under normal conditions you make enough, but in periods of stress (intense exercise, illness, injury, etc.), your demand may exceed what you can produce. In those moments, getting extra glutamine from diet or supplements can be beneficial. (1,2)
Properties: (3)
1. Anabolic, anticatabolic†
2. Stimulates human growth hormone release†
3. Acts as an Antioxidant†
4. Direct fuel for rapidly dividing cells†
5. Immune stimulant†
6. Shuttle for ammonia†
7. Synthesis for purine and pyrimidines†
Role In The Body:
Glutamine wears many hats in our biology. As a building block of protein, it helps repair and build muscle and other tissues. It’s a crucial fuel source for cells of the immune system, like white blood cells. It helps them fight infections and aid in wound healing. Glutamine also supports the digestive system by nourishing the cells that line your intestines. This helps maintain the integrity of the gut barrier. In fact, it’s one of the most essential nutrients for a healthy intestinal lining, often described as “fuel” for your gut cells. Additionally, glutamine plays a role in nitrogen transport and energy production. It can carry nitrogen between organs and participates in metabolic processes that give your body energy. (1,2)
Natural food sources:
The good news is that glutamine is readily found in many high-protein foods. Major dietary sources include meats (beef, pork, poultry), seafood, dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese), and eggs. Plant-based sources, such as beans, lentils, tofu, and vegetables like spinach, cabbage, and beets, also provide some glutamine. If you eat a balanced diet with plenty of protein, you’re likely getting a steady supply of glutamine from your meals. In fact, most healthy people make and consume enough glutamine for their daily needs without thinking about it. (3)
Why do people supplement glutamine?
The main reason is that during times of increased stress on the body, glutamine levels can drop. For example, intense physical exercise can lower blood glutamine temporarily. Some experts theorize this might contribute to immune suppression in overtrained athletes. Similarly, if you’re injured, recovering from surgery, or very ill, your body may be using glutamine rapidly for healing and immune responses.†
In these cases, supplementation may help meet the heightened demand and support recovery. Additionally, people with certain digestive disorders (like inflammatory bowel disease) or those on rigorous training regimens often consider glutamine to aid gut repair and muscle recovery. In short, while glutamine isn’t a “must-have” for everyone, specific situations create a greater need for it. This is why it has become a popular supplement in both the sports nutrition and clinical nutrition worlds.†
![]()
L Glutamine Benefits:
Glutamine wears a lot of “hats” in the body, so it offers a wide range of benefits. Below, we break down the significant glutamine categories’ benefits, with a look at what science says about each.
Glutamine And Your Immune System:
One of the standout benefits of glutamine is how it fuels and fortifies the immune system. Immune cells such as lymphocytes and macrophages use glutamine as a primary energy source. If you become very sick or injured, these cells gobble up glutamine to fight off infections and repair tissues. However, if the supply of glutamine is lower than your body’s needs, your body may break down protein stores, such as muscle. (3,4,5)
Supplemental glutamine may help boost immune function, especially under high physical stress. For example, studies have noted that endurance athletes taking glutamine had a lower incidence of infections and colds after extreme workouts. By providing extra fuel to immune cells, glutamine prevents the steep decline in immune activity that can follow prolonged exercise. As the ISSA (International Sports Sciences Association) notes, glutamine can act as a protective buffer for athletes’ immunity. This helps them stave off the latest bug so they don’t have to skip training. (6)
Glutamine And Gut Health:
Perhaps the most remarkable benefit of L-glutamine is its ability to nourish and repair the gut. If you take nothing else away from this article, remember: glutamine is your gut’s best friend. It’s often the number one supplement recommended for supporting intestinal health. (7)
Glutamine is the primary fuel source for the cells that line your intestines (the enterocytes). These cells turn over rapidly and have high energy needs to keep your intestinal lining intact. By providing fuel to these cells, glutamine helps maintain the strength of the gut barrier. The gut barrier is a thin, one-cell-thick lining that separates your intestinal contents from the rest of your body. A healthy gut barrier allows nutrients to pass into the bloodstream while blocking toxins and harmful microbes. When the barrier is compromised (often called “leaky gut”), it can lead to inflammation and a host of issues. Glutamine helps seal the gut lining by promoting the growth and regeneration of these intestinal cells and by regulating the “tight junction” proteins that hold the cells together. (8)
Additionally, research suggests supplementation may benefit gastrointestinal disorders like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). (9,10,11)
- In Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), a notable clinical trial showed that high-dose oral glutamine (15 g, 3x per day) for 8 weeks led to remarkable improvements. About 80% of the glutamine group achieved major symptom relief, and gut permeability returned to normal levels, whereas the placebo group did not. (12)
- In ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease (types of IBD), glutamine has shown promise in some studies for reducing intestinal inflammation and aiding remission. For example, glutamine supplementation improved intestinal permeability in Crohn’s patients, helping to restore the gut’s barrier function. (13)
- Leaky Gut & general gut repair: Even if you don’t carry a formal diagnosis, issues like chronic bloating, food sensitivities, or alternating constipation/diarrhea can point to a leaky or inflamed gut. Glutamine is often the first supplement recommended to tackle this. It’s been shown to reduce intestinal inflammation and strengthen the mucous layer that protects the gut wall. It’s also frequently used to help heal the gut after antibiotic use, stomach viruses, or chemotherapy, which can all damage the intestinal lining. (14)
Muscle Recovery:
Glutamine first became famous in the bodybuilding community because of its role in muscle recovery. It’s not a steroid or even a direct muscle builder, but rather a tool to help your muscles repair and prevent excessive breakdown (anti-catabolic effect). (2)
When you work out hard, especially with endurance or heavy resistance training, your muscles experience micro-trauma and use up key nutrients. Glutamine levels in muscle can drop after intense training, which might limit optimal recovery. Supplementing with glutamine ensures your muscles and blood have an ample supply to kickstart the repair process. Glutamine helps drive protein synthesis (the rebuilding of muscle tissue) by donating nitrogen to form new amino acids and proteins. It also helps maintain cellular hydration and volume, which is important for muscle repair signals. (15)
If you’re dieting or in a cutting phase, glutamine might help you hold onto your hard-earned muscle even as you lose fat. It does so by maintaining a positive nitrogen balance in muscle tissue and reducing markers of muscle degradation following workouts.†
Additionally, several studies back up glutamine’s role in reducing muscle soreness and improving recovery. In one study, participants who took glutamine (along with leucine) after eccentric exercise had faster recovery and less delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS) compared to a placebo. Another study found that adding glutamine post-workout increased muscle glycogen resynthesis by 16%, keeping glycogen levels higher for hours after exercise. Glycogen is the stored carbohydrate in your muscles that fuels performance. By restoring it faster, glutamine may help fend off fatigue and improve the quality of your next workout. Essentially, more glycogen = more energy for your muscles. (16)
However, it’s important to note what glutamine won’t do: it’s not a powerhouse muscle-builder on its own for well-nourished individuals. If you’re already eating ample protein and calories, taking extra glutamine is not proven to boost muscle strength or mass beyond your normal diet. (17)
Metabolic Support and Cravings Control:
Beyond gut and muscle, glutamine has some intriguing effects on metabolism and cravings that are worth noting:
- Insulin Sensitivity and Blood Sugar: Early research suggests glutamine might improve how the body handles blood sugar. In stressed or ill individuals, glutamine has been observed to enhance insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake. This could be beneficial for metabolic health. Better insulin sensitivity means your cells respond more effectively to insulin, which helps keep blood sugar levels stable. A healthier blood sugar response can aid in weight management and energy levels. (18)
- Reducing Sugar and Alcohol Cravings: As mentioned earlier, glutamine is famous for its ability to reduce cravings. It’s a bit of a biohack that nutritional therapists have used for years. The mechanism is likely due to glutamine’s role as an alternate fuel for brain cells. It can be converted to glucose in the brain, easing the “energy crisis” that triggers a craving. So, when you’re hit with a strong desire for a cookie or a drink, taking a few grams of glutamine may take the edge off within minutes. Real-world tip: If you struggle with afternoon sugar cravings, try stirring 5 grams of glutamine powder into a glass of water and sipping it. Many people find that their craving dissipates quickly as the glutamine stabilizes their blood sugar and feeds the brain. (18)
- Appetite Control: By helping maintain even blood sugar levels and reducing those “must have sugar now” moments, glutamine may indirectly support better appetite control. You might find you’re less likely to reach for a snack between meals because glutamine prevents the rapid drop in blood glucose that often sparks hunger. (18)
Heart Health, Liver Detox, and More (Emerging Areas):
Beyond the well-established benefits above, glutamine has some emerging roles in other organ systems:
- Cardiovascular Health: Early research indicates glutamine may have cardio-protective effects. Some studies in hypertensive animals and humans have noted that glutamine supplementation can lower blood pressure and reduce markers of inflammation. (19)
- Antioxidant Production (Glutathione) and Liver Support: Glutamine is a precursor for glutathione, which is one of the body’s most powerful antioxidants. Your liver uses glutathione to detoxify chemicals and repair oxidative damage. Glutamine, along with cysteine and glycine, is needed to manufacture glutathione. So by providing glutamine, you indirectly support your liver’s detox capacity and antioxidant defenses. (20)
- Kidney Support (Ammonia Removal): Glutamine plays a role in neutralizing ammonia, a toxic byproduct of protein metabolism. It does this by carrying ammonia to the kidneys, where it can be excreted. The amino group in glutamine essentially locks onto ammonia to form glutamate, which the kidneys then safely handle. (21)
- Brain and Mental Health: Although the main neurotransmitter is glutamate (not glutamine), the two are closely related. Glutamine can cross the blood-brain barrier and then convert to glutamate in the brain, influencing the balance of excitatory and calming signals. (22)
![]()
How to Take L-Glutamine (Dosage & Usage Guide)
Glutamine is available as a dietary supplement in a few forms, and the way you take it can influence its effectiveness. Here’s your guide to using glutamine:
Forms Available:
The most common forms of L-glutamine on the market are powder and capsules. Powder is very popular because it’s easy to mix into shakes, drinks, or even just water, and it allows flexible dosing (you can scoop 5 grams or 10 grams as needed). Pure glutamine powder is tasteless and dissolves well, making it simple to add to your post-workout protein shake or your morning glass of water.†
Capsules are essentially glutamine powder pre-measured in pill form (often 500 mg or 1000 mg per capsule). These are convenient if you’re traveling or if you just dislike the process of mixing powders. For example, one product offers 500 mg vegetarian capsules, and you can take a couple at each meal instead of a scoop of powder. Neither form is inherently “better” – it’s about convenience and how you plan to use it. If you need higher doses (for gut healing, etc.), powder is often more practical.†
General Dosage Range:
For general health or fitness purposes, typical dosing is 5 to 10 grams per day. A common approach is 5 g (about one teaspoon of powder) taken once or twice daily. This kind of moderate dose is often enough to support recovery for regular exercise or to maintain gut health. If you’re targeting intensive gut healing or immune support, doses can go higher – often 15 to 20+ grams per day, split into multiple servings.†
In clinical trials for IBS, doses around 15-30 g per day have been used effectively without issue. For example, an average therapeutic dose for Crohn’s disease was about 30 g daily in one study. That said, when using higher doses, it’s wise to ramp up gradually. Always start on the lower end (e.g., 2–5 g per day) and see how your body responds. If well-tolerated, you can build up the dose every few days. (12,13)
Splitting larger doses (over 10 g) into 2-3 servings is important, as your gut will absorb smaller amounts more efficiently than one huge dose. For instance, instead of 20 g at once, do 10 g in the morning and 10 g in the evening. This also helps avoid any mild GI upset from a big single dose.†
Timing Recommendations:
When is the best time to take glutamine? It depends on your goals, but here are some common timing strategies:
- Post-Workout (for Recovery): Taking ~5 grams of glutamine shortly after exercise (within 30 minutes) is a popular protocol to replenish depleted glutamine stores and jumpstart muscle recovery. Many athletes will mix glutamine into their post-workout protein shake or recovery drink. This is considered a priority time because your muscles are most in need then. Some evidence suggests this can reduce soreness and improve recovery of strength.†
- Between Meals (for Gut or Immune Benefits): For gut healing and immune support, empty stomach dosing is thought to maximize absorption by the gut and uptake by immune cells. A common recommendation is to take glutamine first thing in the morning (before breakfast) and/or between meals when your stomach is relatively empty.†
- With or Without Food: If you experience any stomach upset taking glutamine by itself (some people report slight bloating on an empty stomach), you can absolutely take it with a small meal or mixed into something like a protein shake.†
- Duration of Use: How long should you supplement glutamine? This depends on your goals. For workout recovery or immune support during a training season, you might use it continuously throughout intense training periods. For gut issues, glutamine isn’t a one-and-done; you’ll want to use it daily for at least 2–3 months to gauge full benefits (often 4+ months for significant gut healing). Many protocols suggest a duration of ~12 weeks, after which you can reassess whether you can taper down. Glutamine is not known to require “cycling” on and off like some supplements. It can be used long-term if it continues to help you.†
![]()
Popular Products:
Ready to give glutamine a try? Below are some popular L-glutamine supplements on the market and what makes them stand out.
- Nutricost L-Glutamine (Powder / Capsules)
- AllMax Nutrition Glutamine Powder
- NOW Foods L-Glutamine (Veg Capsules)
- Nutrex Glutamine Drive
- Hi-Tech Pharmaceuticals L-Glutamine
Nutricost L-Glutamine:
- What it is: Straightforward, budget-friendly L-glutamine available as an unflavored powder or convenient capsules.†
- Best for: Anyone wanting value + flexibility. Powder is great if you use 5–10 g/day; capsules make it easy to take small amounts between meals.†
- Why we like it: Clean, no-frills glutamine with multiple size options so you can keep costs down if you take it daily.†
How To Take Nutricost Glutamine:
- Capsules: Take 1 capsule 1-3 times daily on an empty stomach with 8-12 oz of water or as directed by your healthcare professional.
- Powder: As a dietary supplement, mix 1 scoop daily with 6-10 oz of water or as directed by your healthcare professional.
AllMax Nutrition:
- What it is: Micronized L-glutamine powder designed to mix easily.†
- Best for: Lifters and endurance athletes who want smooth mixing and a reputable sports-nutrition brand.†
- Why we like it: Micronization helps it dissolve quickly in water or shakes—handy for intra/post-workout use.†
How To Take AllMax Nutrition Glutamine:
The manufacturer recommends mixing one (1) rounded teaspoon (5g) in water or juice once daily. For training sessions and athletic events, take approximately 30 minutes prior to training and immediately after training to help prevent muscle tissue breakdown and aid muscle recovery. At times when you are not training, mix 1 rounded teaspoon (5g) in water or juice approximately 45-60 minutes prior to meals.
NOW Foods:
- What it is: Vegetarian capsules with pure L-glutamine—great if you prefer pills over powder.†
- Best for: People focused on gut health who like smaller, more frequent servings; travelers; anyone avoiding powders.†
- Why we like it: Easy to tailor dose (e.g., 1–2 caps before meals) and from a long-standing wellness brand.†
How To Take NOW Foods L-Glutamine (Veg Capsules):
The manufacturer recommends taking one (1) capsule 1 to 3 times daily, preferably between meals. Store in a cool, dry place after opening.
Nutrex:
- What it is: Unflavored powder positioned for daily recovery.†
- Best for: Athletes wanting a simple, consistent routine for muscle recovery and immune support.†
- Why we like it: Clear usage guidance (morning/bedtime) fits the recovery window most people can stick to.†
How To Take Nutrex Glutamine Drive:
The manufacturer recommends mixing one (1) scoop with 6-8oz of water or any beverage of your choice. They also suggest taking two (2) servings daily; one in the morning upon rising and one before going to bed. On training days, you may want to take an extra serving following your workout.
Hi-Tech Pharmaceuticals L-Glutamine
- What it is: Pharma-grade L-glutamine from a performance-focused brand.†
- Best for: Gym-goers who already use Hi-Tech products and want a high-purity glutamine to slot into their stack.†
- Why we like it: Reliable quality and stack-friendly for post-workout or bedtime protocols.†
How To Take Hi-Tech Pharmaceuticals Glutamine:
Mix a scoop of Glutamine Powder with 8oz. (230ml) water or your favorite beverage, or use as directed by a physician or licensed nutritionist.
![]()
Glutamine FAQs:
You’ve learned a lot about glutamine’s uses, but you might still have some specific questions. Let’s address some common FAQs to clear up any remaining confusion:
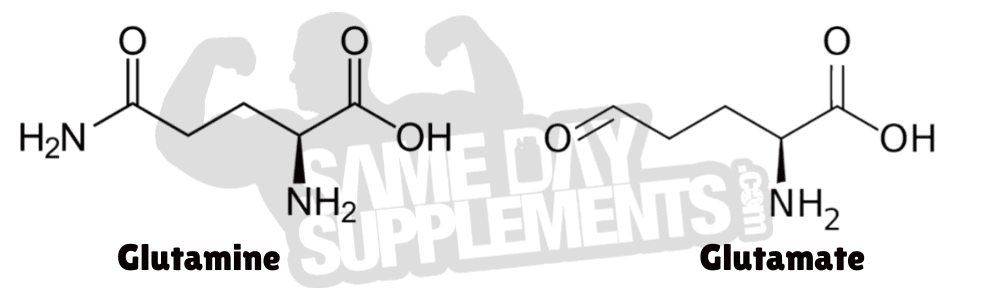
What’s the difference between L-glutamine and glutamate (glutamic acid)? |
|---|
| Glutamine and glutamate are related, but distinct, amino acids. Think of them as cousins in the amino acid family. Glutamate (aka glutamic acid) is a non-essential amino acid that serves as the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. L-glutamine can be thought of as the transport form. It can travel through the bloodstream and cross into the brain, where it may be converted into glutamate as needed. Outside the brain, glutamate is actually a byproduct of glutamine metabolism (for instance, when the gut or kidneys use glutamine, glutamate is produced). One key difference is that glutamate cannot freely cross the blood-brain barrier on its own. (23)
|
Can glutamine improve my mood or cognitive function? |
| Glutamine is not a proven mood enhancer in the way, say, an anti-anxiety drug or a stimulant is. However, there are a few interesting connections. Glutamine’s support of gut health can indirectly improve mood – a healthier gut often translates to better production of neurotransmitters like serotonin (hence the gut-brain axis influence). Also, glutamine’s ability to stabilize blood sugar can prevent those cranky low-blood-sugar moments that affect mood. (18)
On the research side, some early studies looked at glutamine in neurological conditions and even in fatigue and depression. Because glutamine can increase the production of the calming neurotransmitter GABA (via conversion from glutamate), some practitioners refer to it as “the calming amino acid” for anxious individuals. But it’s not a guaranteed brain booster for everyone. For the average person, a normal glutamine dose is unlikely to have a strongly noticeable effect on mood, aside from the benefits of better overall health (e.g., if your gut feels better, you may feel better emotionally). (24,25) |
Will glutamine help me lose weight or burn belly fat? |
Not directly, no. Glutamine is not a fat-burner in the way thermogenic supplements or stimulants are. You won’t take glutamine and suddenly see fat melt away. That said, glutamine can assist your weight loss efforts in a few indirect ways:
|
I already take whey protein or BCAAs after workouts. Do I need glutamine too? |
Whey protein actually contains glutamine naturally. So if you’re having protein shakes, you’re already getting some glutamine. BCAA supplements (branched-chain amino acids) typically do not contain glutamine unless the label specifically says so. BCAAs usually only include leucine, isoleucine, and valine. However, some workout supplements are hybrids that add glutamine on top of BCAAs.†
|
![]()
Supplements With Glutamine:
When it comes to amino acids, you have the fortunate opportunity to get them from a variety of sources. Likewise, glutamine can be supplemented on its own or with other blends. In this section, we’re going to dive into some popular intra and post-workout supplements that feature glutamine.
Scivation Xtend BCAA:

Electrolyte Blend:
This blend of potassium and sodium can help maintain hydration and promote muscle repair. (28,29,30)
Citrulline Malate:
Citrulline Malate combines the nonessential amino acid L-Citrulline and Malic Acid. This amino acid plays a role in improving exercise performance and widening your blood vessels, which may aid in improving muscle growth. (31,32)
How To Take Scivation Xtend BCAA:
The manufacturer recommends mixing two (2) scoops daily in 10-14 fl. oz. of water (adjust for taste preference) and shaking well.
- On training days: Mix one (1) scoop during exercise and one (1) scoop after exercise.
- On non-training days: Mix two (2) scoops throughout the day.
Customer Review By Mathew: “Fruit Punch is our favorite, & it really helps for workouts, just can’t do without it, but for some reason unable find the 90 servings locally, so was happy to find this store. It arrived quickly, which was great since low on our existing batch, so this is our go to supplier going forward.”
NutraKey BCAA Optima:

Taurine:
Taurine is an amino acid found commonly in the brain. It serves multiple purposes in the body, including (33):
- Maintaining hydration and electrolytes
- Regulates minerals such as calcium
- Supports the nervous system and eyes
- Regulate immune system functions
But taurine also may boost exercise performance. Studies suggest that taurine may aid in removing waste products that lead to fatigue and muscle burn. This translates to it being effective in promoting endurance, increasing alertness, and enhancing recovery. (34)
How To Take Nutrakey BCAA Optima:
The manufacturers recommend mixing one (1) scoop with 8-12 oz. of water before your workout and one (1) scoop with 8-12 oz. of water an hour after your workout. However, you may want to adjust the servings based on your lifestyle. The manufacturers recommend casual-light activity, take one (1) scoop post-workout. Users with a more moderate weekly activity level may want to take one (1) scoop post-workout and one (1) scoop before bed. Athletes may want to take one (1) scoop with a meal and one (1) scoop before and after a workout.
Customer Review By Robert: “These BCAA’s are great! Taste great and gets the job done. Highly recommended!”
USP Labs BCAA Supreme:

Alanine:
Alanine or beta-alanine is a popular ingredient for pre-workouts because beta-alanine can help aid performance. This amino acid can help buffer away lactic acid build-up, which is associated with the “burn” effect of training a muscle. For these benefits, you would need around 2-5 grams of beta-alanine. (35)
Glycine:
In addition to being an amino acid, the body uses glycine to make glutathione (an antioxidant), which is a component of creatine and collagen. This ingredient may help enhance cognitive function, lower blood pressure, and control blood glucose. (36)
L-Lysine HCl:
Lysine is another amino acid that can play a role in protein synthesis. It also helps hormone and enzyme production and other functions. (37,38)
Sustamine™:
Sustamine™ is a combination of two amino acids, L-glutamine and L-alanine. This combination has potential protective, absorption-enhancing activities and even inhibits muscle protein catabolism (muscle breakdown). (39)
How To Take USP Labs BCAA Supreme:
The manufacturers recommend mixing one (1) serving (2 level scoops) in 20 ounces of water and shaking vigorously for 30 seconds. Sip throughout a workout, athletic event, or any time additional amino acids are needed. Due to high leucine content, some initial foaming may occur, which should subside over a few minutes with light shaking. Shake the container before each use to disperse ingredients that may have settled.
Customer Review By Jacob: “Just got it today. Rocket Pop flavor tastes great. Powder mixes well.”
![]()
Wrapping Up!
And this marks the end of our post on Glutamine. Thank you for reading! And as always, if there was something that wasn’t clear, another question you might have, or if you have another idea for a blog, Email Us!
Are you looking for more to read? Check out our other blogs!
- Creatine 101
- What Is NAC?
- What Is Whey Protein?
- Natural Testosterone Boosters Guide
- The Best Tongkat Ali Supplements For You
- How To Build Muscle With Turkesterone
![]()
Side Effects And Warnings:
Do not exceed the recommended daily dose. Consult a physician prior to use if you have any medical conditions. Intended only for adults 18 years and older. Not for use by those who are pregnant, trying to become pregnant, or nursing.
![]()
Disclaimer:
†Please note the intention of the information provided is for reference only. Furthermore, we are in no way providing medical advice or instruction. Instead, the information provided in this guide/blog utilizes anecdotal information and available studies/reviews. While we aim to maintain and display accurate information, we can’t guarantee it represents the latest product formulation or information. Therefore, please visit the manufacturer’s website if you have any concerns. Also, the information above does not represent our views here at Same Day Supplements. Instead, these are the manufacturers’ and users’ views and information. Additionally, the Food and Drug Administration has not evaluated these statements. Finally, these products aim not to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent disease or illness.