Vitamin D, Am I Getting Enough?
What Is Vitamin D | What Effects My Absorption | Vitamin D RDA | Is Sun Exposure Enough | Food Sources Of Vitamin D | Popular Products | Too Much Vitamin D | Warnings And Side Effects | Disclaimer
Winter blues got you down? Feeling sluggish despite getting enough sleep? You might be missing a crucial ingredient for sunshine and good health: Vitamin D. This essential nutrient, often called the “sunshine vitamin,” plays a vital role in everything from bone health to immune function and mood. But with the days getting shorter and colder, many of us face a silent threat – vitamin D deficiency.
Worried you might not be getting enough? This guide will equip you with everything you need to understand vitamin D, identify potential deficiencies, and explore safe ways to boost your intake.
![]()
What Is The Role of Vitamin D?
As we mentioned, vitamin D is an essential nutrient, but it is present in very few foods. Vitamin D is essential for absorbing calcium, keeping your bones strong, and supporting your immune system. But its benefits go beyond just the skeleton. Vitamin D plays a role in cell growth, inflammation reduction, and even mood regulation. (1,2,3) It is a fat-soluble vitamin, meaning absorption takes place along with fats in your diet.
Additionally, the body can store vitamin D in fatty tissue. Because of this, recommendations for vitamin D are typically smaller to maintain good health compared to other vitamins.
Two forms, one goal: There are two main types of vitamin D: D2, found in plant sources like mushrooms, and D3, produced by our skin when exposed to sunlight. While both contribute, D3 is generally more efficient at boosting your levels. But a couple of factors can undermine how it is absorbed.
![]()
What Effects My Absorption Ability?
During sun exposure, sunlight 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin absorbs UVB radiation. This chemical then converts to pre-vitamin D3, which isomerizes into vitamin D3. The liver and kidneys can metabolize vitamin D to its primary circulating form. Unfortunately, Sun-induced vitamin D is greatly influenced by seasons, time of day, latitude, altitude, air pollution, skin pigmentation, sunscreen use, passing through glass and plastic, and aging. (4)
Where You Live:
If you live closer to the equator, you likely have higher absorption of the vitamin through the sun’s UVB light. Consequently, areas further from the equator, like New York, receive less UVB light exposure. In addition, during the fall to winter months, the days become shorter, and so does the emission of UVB rays. (5)
Melanin:
Melanin is the substance in your skin that makes it dark. UVB rays penetrate the skin to kick-start the body’s vitamin D production. These two substances compete; as a result, darker-skinned people generally require more UVB light to produce the same amount of vitamin D as lighter-skinned people.†
Temperature:
Warm skin is a better coefficient for vitamin D production than cooler skin. So hotter days will likely produce more vitamin D than colder ones.†
Age:
As you age, the conversion process in your skin that converts UVB rays decreases. Due to this, older people may not produce vitamin D as efficiently as younger people.†
Co-factors:
Making sure you have sufficient vitamin D co-factors( vitamin K2, magnesium, boron, and zinc) is essential for optimal production of the vitamin and overall health. For example, magnesium is essential in the metabolism of vitamin D. However, when you take large doses of vitamin D, you can induce severe depletion of magnesium. (6)
![]()
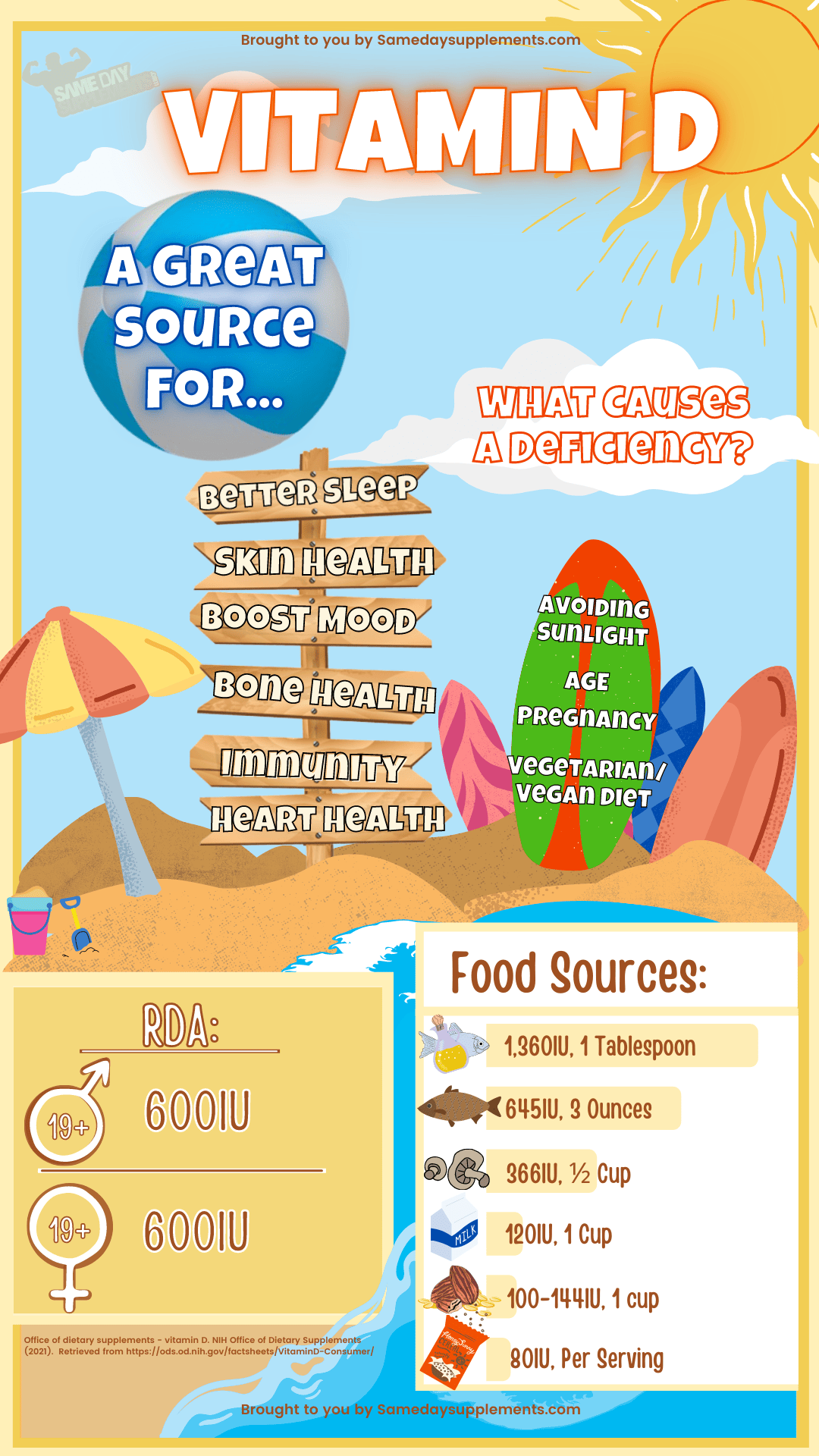
How Much Vitamin D is Recommended?
Recommendations from the US Institute of Medicine suggest that an average daily intake of 400–800 IU, or 10–20 micrograms, is adequate for 97.5% of individuals (7,8). However, this value may change depending on your exposure to sunlight, as well as some of the factors above. In some people, levels of 1000–4000 IU, or 25–100 micrograms, are considered sufficient(9). The bottom line is that if you feel you may not be getting an adequate amount of any vitamin, you should see your doctor and request to get a blood test.
The Institute of Medicine (IOM) and the Nordic Nutrition Council base their recommendations on the following blood levels(7,10):
- Sufficient: 25(OH)D greater than 20 ng/ml (50 nmol/l).
- Insufficient: 25(OH)D less than 20 ng/ml (50 nmol/l).
- Deficient: 25(OH)D less than 12 ng/ml (25 nmol/l).
![]()
Is Getting Vitamin D From The Sun Enough?
D vitamins exist in two forms. One form, Vitamin D2, is obtained from the UV irradiation of the yeast sterol ergosterol and is found naturally in sun-exposed mushrooms. UVB light from the sun strikes the skin, and humans synthesize vitamin D3, so it is considered the most “natural” form. (11)
Despite this, you may not be receiving enough of the vitamin from the sun. If you live in an area further from the equator and spend most of your day indoors, you may want to look into supplementing your vitamin D intake with foods and supplements.
Although the sun is considered the most natural source of this vitamin, dermatologists advise against tanning in order to get this vitamin. To protect your skin, use sunblock while outdoors in bright sunlight or for long periods. (12)
What Are Food Sources? (13)
Eating plenty of vitamin-D-rich foods is a great way to ensure you get enough of this essential nutrient, especially if you spend most of your day indoors.
Fish are great source of Vitamin D:
- Cod liver oil
- Rainbow Trout
- Salmon
- Sardines
- Tuna
And some great alternatives to fish include:
- Mushrooms
- Fortified Milk (including soy, almond, or oat milk)
- Fortified Cereal
- Eggs
![]()
Vitamin D Supplements:
If you weren’t prescribed to take vitamin D as a standalone supplement but feel you aren’t getting an adequate amount of it in your diet, you can consider taking a multivitamin.
- Opti Men By Optimum Nutrition has 1,500 IU per 3 tablets
- Opti-Women By Optimum Nutrition has 600 IU per 2 tablets
- Animal Pak By Universal Nutrition has 680 IU per 2 packs
- Daily Formula By Universal Nutrition has 400 IU per Tablet
How To Take Opti Men By Optimum Nutrition:
The manufacturers recommend men take 3 tablets daily with food.
Opti Men Review By Andre: “Excellent multivitamin, I have been taking it for years and it is one of the best.”
When selecting a vitamin D standalone, it’s important to know which IU your doctor recommends for you. More IUs are not necessarily better.
- Now Foods Vitamin D ranges from 400 IU to 10,000 IU
- Healthy Origins Vitamin D offers a 10,000 IU supplement at 360 soft gels per bottle
- 21st Century Vitamin D features a 5,000 IU supplement as 360 tablets per bottle
- Kirkland Vitamin D features a 2,000 IU supplement at 600 soft gels per bottle
How To Take Now Foods Vitamin D-3:
The manufacturers recommend taking 1 soft-gel daily with a meal.
Now Foods Vitamin D Review By Ana: “Ótima qualidade, ótimos resultados, recomendo. (Great quality, great results, I recommend. )”
![]()
Can I Have Too Much?
As we mentioned above, the recommended dosage has fluctuated over the years. But according to Yale Medicine, 600 IU per day should be enough for healthy individuals. For people 70 years old and older, 800 IU should be sufficient (14).
Too much of this vitamin can result in toxicity, also called hypervitaminosis D. Toxicity is usually caused by mega doses of this vitamin in supplements, not by diet or sun exposure. The main consequence of this toxicity is a buildup of calcium in your blood (hypercalcemia), which can cause nausea and vomiting, weakness, and frequent urination. Symptoms might progress to bone pain and kidney problems, such as the formation of calcium stones.
Treatment includes stopping vitamin D intake and restricting dietary calcium (15).
![]()
Wrapping Up!
And this marks the end of our post on Vitamin D. Thank you for reading! And as always, if something was not clear, you have another question on this topic, or if you have another idea for a blog, Email Us!
Are you looking for more to read? Check out some of our other blogs!
- Creatine 101
- Natural Testosterone Boosters Guide
- The Best Tongkat Ali Supplements For You
- Top Immune System Boosters You’re Missing Out On
- What Is NAC?
- Vitamin C: What Are The Benefits And How You Can Avoid A Deficiency
![]()
Warnings And Side Effects:
If you are pregnant, nursing, or taking any medications, consult your doctor before use. Discontinue use and consult your doctor if any adverse reactions occur.
Keep out of the reach of children. Store at room temperature, tightly closed. Avoid excessive heat.
![]()
Disclaimer:
†PLEASE NOTE: The intention of the information provided is for reference only. Furthermore, we are in no way providing medical advice or instruction. Instead, the information provided in this guide/blog is based on anecdotal information and available studies/reviews. While it is our goal to maintain and display accurate information, we can’t guarantee it represents the latest formulation of the product or information. Therefore, if you have any concerns, please visit the manufacturer’s website. Also, the information above is not a representation of our views at Same Day Supplements. Rather, these are the views and information provided by the manufacturers and users. The Food and Drug Administration has not evaluated these statements. Finally, the intention of these products is not to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease or illness.