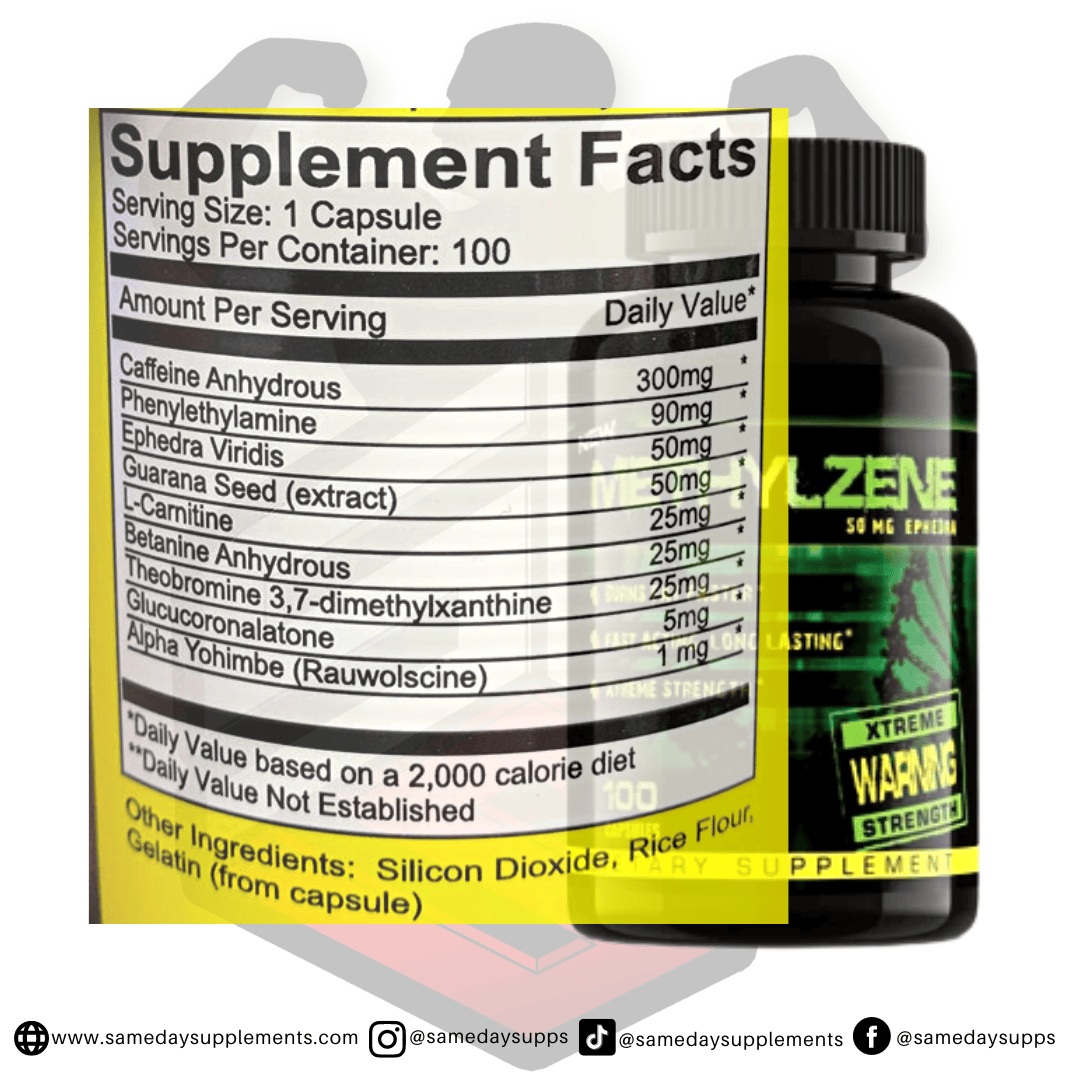
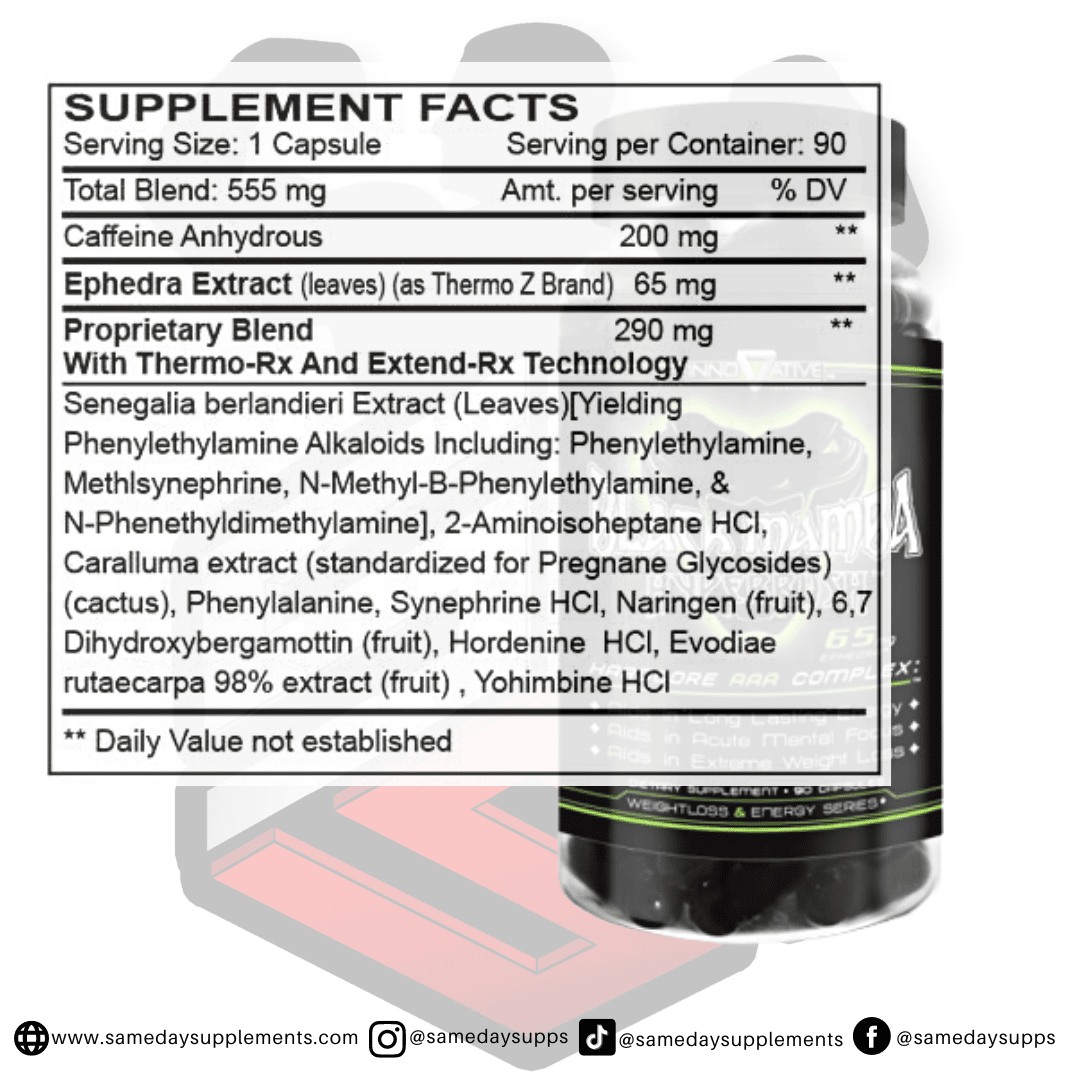
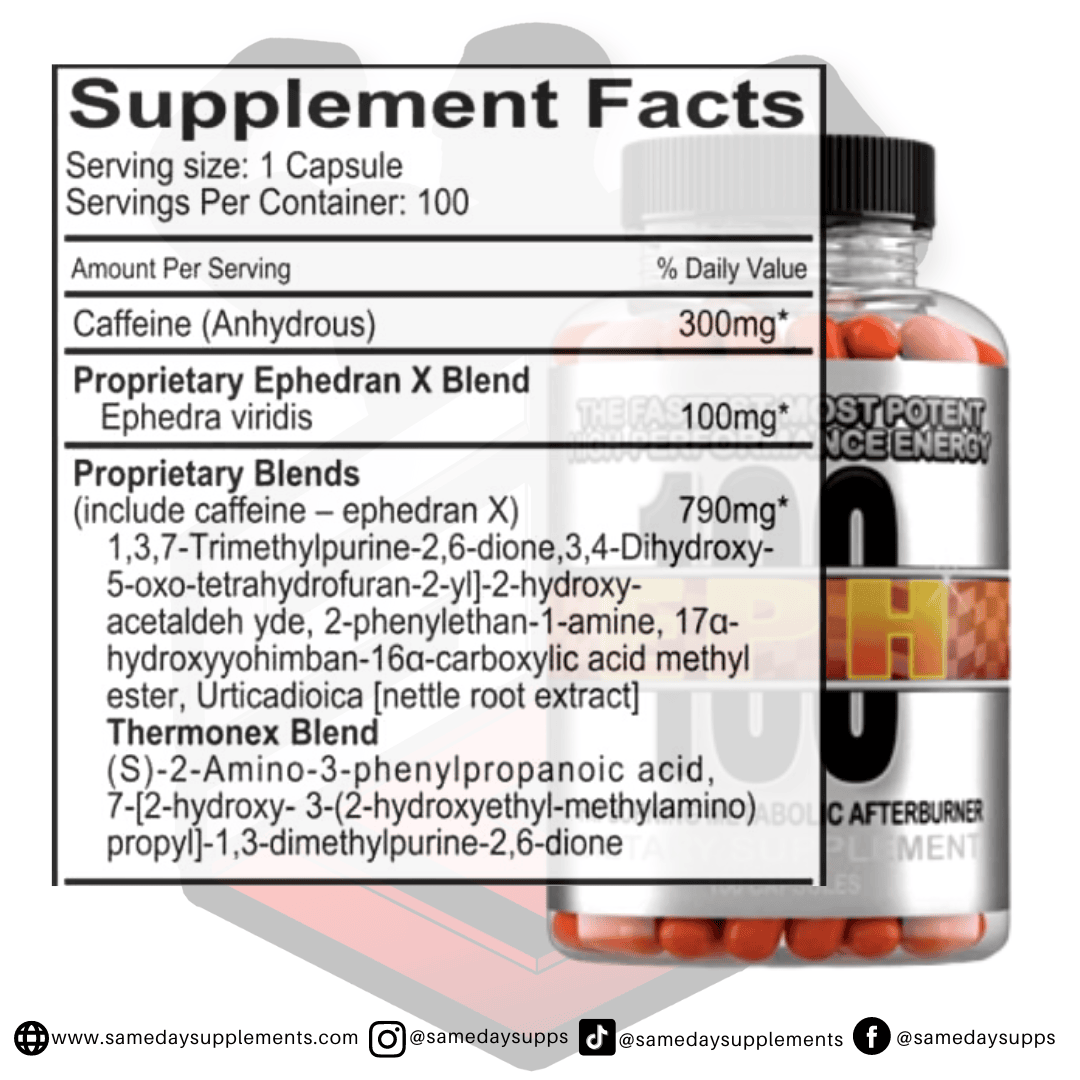
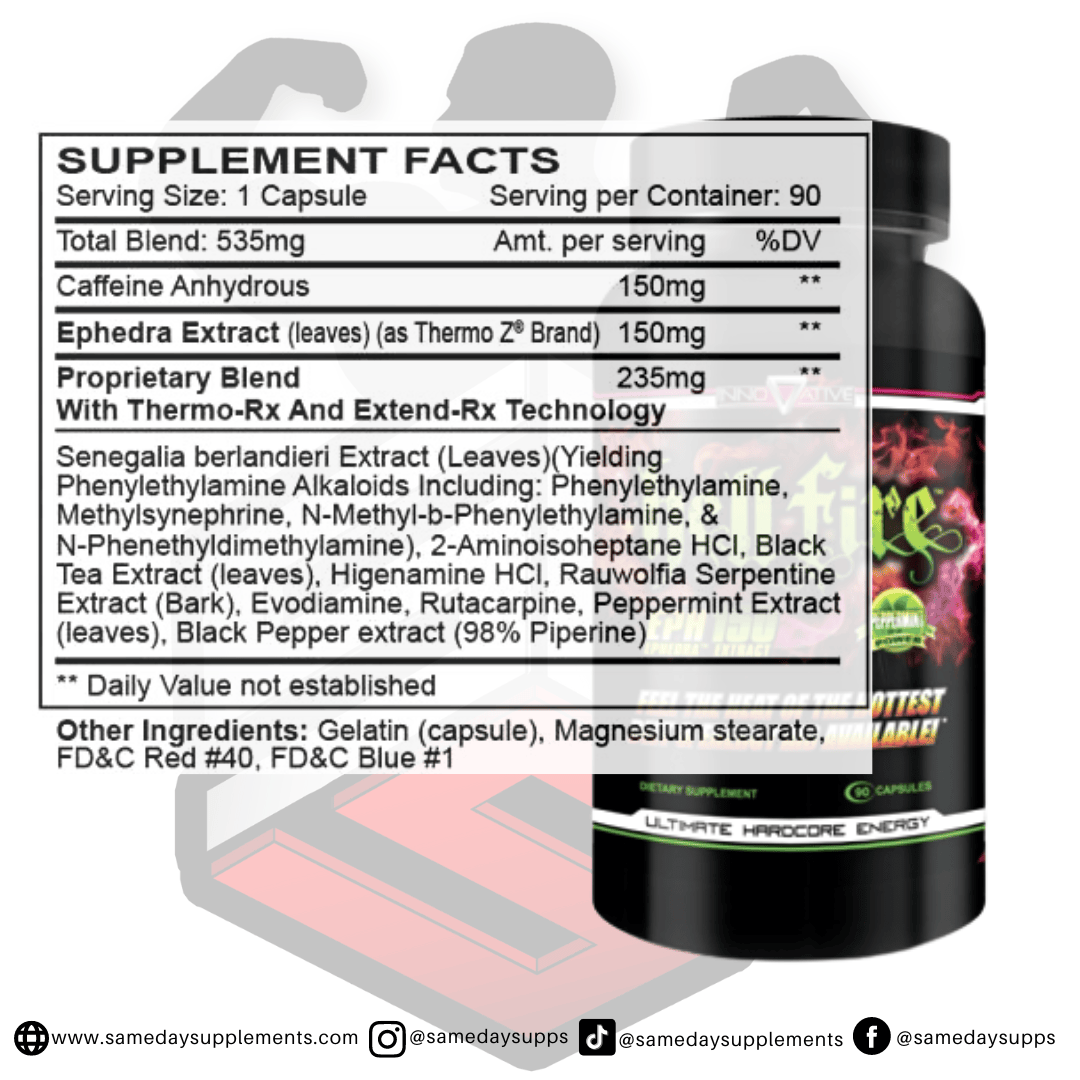
Ephedra Pills Vs Ephedrine: The Biggest Differences Today
📖 Table of Contents
Ephedra and ephedrine are two compounds with uses in traditional medicine for centuries to treat various ailments, including asthma, bronchitis, and respiratory problems.† In recent years, they have gained popularity as dietary supplements for weight loss and athletic performance enhancement. However, the use of these substances has been controversial due to safety concerns and adverse health effects.
In this blog, we will provide an overview of ephedra and ephedrine, their potential benefits and risks, and why ephedrine is no longer available in dietary supplements. We will also address common questions about ephedra and ECA stacks (ephedrine, caffeine, and aspirin) and discuss the legal status of these substances in different countries.
Whether you are considering using ephedra and ephedrine for weight loss or athletic performance or want to learn more about these compounds, this blog will provide you with the information you need to make an informed decision about their use.
🌿 Ephedra vs Ephedrine – At a Glance
- Ephedra (Herbal Source):
- A plant known as Ma Huang, used in traditional Chinese medicine†
- Contains multiple alkaloids: ephedrine, norephedrine, pseudoephedrine, methylephedrine, and others†
- Sold historically as a dietary supplement for fat loss and performance†
- Acts as a natural thermogenic, supporting metabolism, endurance, and appetite suppression†
- Ephedrine (Isolated Compound):
- A single stimulant alkaloid derived from ephedra (or made synthetically)†
- Used in medications as a bronchodilator and decongestant (e.g., asthma, bronchitis, congestion)†
- Can increase metabolism, energy expenditure, and fat oxidation†
- Banned by the FDA as a dietary supplement due to safety concerns†
- Key Difference:
Ephedra = a plant with a mix of alkaloids.
Ephedrine = one isolated stimulant compound (natural or synthetic).
†These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA. Not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
![]()
What Is Ephedra?
Ephedra, also known as Ma Huang, is a plant used in traditional Chinese medicine for thousands of years. The plant contains several active compounds, including ephedrine, pseudoephedrine, and phenylpropanolamine, which are believed to have medicinal properties.
In modern times, ephedra has become popular as a dietary supplement for weight loss and athletic performance enhancement. The plant may have thermogenic properties, which means it can increase metabolism and energy expenditure, leading to weight loss. Ephedra is also believed to improve athletic performance by increasing endurance and reducing fatigue.†
Some of the other names it goes by include:
- Belcho
- Cao Mahuang
- Desert Herb
- Efedra
- Éphédra
- Ephedra sinensis
- Ephedra sinica
- Mormon Tea Leaf Powder
⚠️ Important note: In 2004, the U.S. FDA banned the sale of dietary supplements containing ephedra alkaloids due to safety concerns. Similar bans exist in Canada, Europe, and Australia. Today, products marketed as “ephedra extract” often contain ephedra viridis or stimulant alternatives that do not include ephedrine alkaloids. Consumers should be aware of this difference when reading supplement labels.
What Is Ephedrine?
Ephedrine is a stimulant alkaloid derived from the ephedra plant. Unlike ephedra, which contains multiple active compounds, ephedrine is a single isolated compound with uses in various medications for its bronchodilator and decongestant properties. It is commonly used to treat asthma, bronchitis, and nasal congestion.
Ephedrine has also been used as a weight loss supplement and athletic performance enhancer due to its ability to increase metabolism and energy expenditure. However, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has banned the use of ephedrine as a dietary supplement in the United States by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) due to its potential health risks.
But there are other alkaloids in the ephedra plant, including (1)
Besides ephedrine, the ephedra plant contains several related compounds, including:
- Ephedrine
- Norephedrine
- Pseudoephedrine
- Norpseudoephedrine
- Methylephedrine
- Methylpseudoephedrine
Some of these, like pseudoephedrine, are widely used in over-the-counter cold medicines (e.g., Sudafed) but are regulated due to their potential use in illicit drug production. (2)
So what’s the difference between herb-sourced ephedrine VS synthetic ephedrine?
Synthetic ephedrine differs from herb-based ephedra in one important way: it delivers a precise, measurable dose. Research shows that synthetic ephedrine is rapidly absorbed, reaching peak levels in about an hour. By contrast, ephedra plant extracts vary in potency depending on plant species, growing conditions, and preparation. (3)
![]()
Why The Switch?
On February 9, 2004, the FDA officially banned dietary supplements containing ephedrine alkaloids. This decision followed years of clinical research, safety evaluations, and hundreds of reports of serious side effects. The main concerns included cardiovascular problems such as high blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, palpitations, strokes, and even heart attacks. (4,5)
But here’s an important point about stimulants in general:
Most stimulants (not just ephedrine) have vasoconstrictive effects—they tighten blood vessels. This can naturally raise blood pressure and strain the heart. The effect depends largely on the dose:
- Lower doses (e.g., 25–50 mg medicinal ephedrine) may act as a bronchodilator and decongestant, which is why ephedrine has been used in asthma and cold medications.(6)
- Higher doses can cross the line into unsafe cardiovascular stress, with elevated heart rate, blood pressure spikes, and increased risk of adverse events.
This dose-dependent effect is not unique to ephedrine—it’s true for many stimulants, which is why healthcare guidance is critical before using any stimulant-heavy supplement if you have a heart condition. (6)
So, Is Ephedrine Legal?
The answer is yes—but with strict limits. Ephedrine remains legal in the U.S. as an ingredient in over-the-counter medications for nasal decongestion or asthma, but it is highly regulated. You’ll find it behind the counter at most pharmacies in specific dosages and only for approved medical use. It should never be used casually for weight loss or performance enhancement without medical supervision.
For athletes, it’s also worth noting that ephedrine and all related stimulants (including ephedra and their optical isomers) are prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA). That means professional and competitive athletes risk disqualification if they test positive for it. (7)
![]()
What To Expect:
Stimulants like ephedra have long been used for their potential weight-loss benefits and performance-enhancing effects. That’s why ephedra-based supplements are still popular today.
Some of the most recognized effects include:
- Appetite Suppression – helping reduce cravings and daily calorie intake.†
- Boosting Metabolism – promoting greater calorie burn, even at rest.†
- Increased Energy – supporting workouts and daily activity levels.†
The ECA Stack
Traditionally, ephedrine was paired with caffeine and aspirin in what became known as the ECA Stack. This combination was popular for weight loss and performance support:
- Ephedrine + Caffeine: Both stimulate the central nervous system, triggering the release of norepinephrine—a key neurotransmitter for “fight or flight” responses. Together, they improve alertness, raise energy, and enhance metabolic rate. (8)
- Aspirin: Functions as a pain reliever, but in the stack, it also helps sustain norepinephrine activity, extending the stimulant effects.†
But was it effective?
Research shows that ephedrine by itself is effective for fat loss, but in studies of the ECA stack, participants lost about two extra pounds per month compared to placebo. (8) While this may sound modest, it was considered a clinically significant result.
When it comes to performance, the evidence is less conclusive. However, the same review noted that ephedra plus caffeine was just as effective as ephedrine plus caffeine for weight loss outcomes. (8)
![]()
Is There Anything Stronger?
When people think of ephedra, they usually think of ephedrine—but that’s only one small part of the plant. In fact, ephedrine makes up just 0.5–2.5% of the herb. Even without ephedrine, ephedra is packed with other bioactive compounds that may contribute to its stimulatory and metabolic effects. (9,10,11)
What’s Left in Ephedra (Without Ephedrine):
- Epicatechins – Also found in dark chocolate, epicatechins belong to cocoa flavonols. Research suggests they may: (12,13,14,15)
- Improve blood flow†
- Enhance insulin sensitivity†
- Support appetite suppression†
- Lower cholesterol†
- Aid muscle growth by inhibiting myostatin, a protein that limits muscle development.†
-
Polyphenols & Glycosides – These antioxidant compounds can improve nutrient absorption and cellular communication, which may enhance how well your body responds to other active ingredients in fat burners. (16)
- Catechins – Commonly found in green tea, catechins are widely studied for their role in fat oxidation and weight loss. (17)
- Ephedrans (Glycans) – These carbohydrate-based compounds help stabilize cell-to-cell interactions. In animal studies, ephedrans lowered blood glucose levels in both normal and diabetic mice. While more research is needed in humans, they may represent another potential pathway for fat loss. Ephedra also contains ephedrans, aka glycans. Glycans function as a protective stabilizer for cell-to-cell interactions. (18,19)
- Tannins (Gallic Acid) – Known for giving wine its dry taste, gallic acid has been shown to help regulate weight and blood glucose levels (20). It may also inhibit enzymes that break down drugs, allowing certain compounds to stay active longer in the body (21).
Even without ephedrine, these components contribute to ephedra’s stimulating, thermogenic, and metabolic effects.
How Does Ephedrine Work:
Ephedrine itself is a sympathomimetic compound. That means it mimics the effects of the sympathetic nervous system—the “fight-or-flight” response. It increases the release of adrenaline and noradrenaline, which can lead to: (22)
- Increased heart rate†
- Higher blood pressure†
- Elevated metabolic rate†
- Strong bursts of energy and alertness†
✅ Key Takeaway: Even without ephedrine, ephedra is not “empty.” It still contains multiple compounds—like catechins, epicatechins, and glycosides—that may support metabolism, fat oxidation, and overall stimulant effects. Today’s ephedra-based fat burners are formulated to leverage these properties alongside other added stimulants, making them viable (and still very strong) options in the fat-burner world.†
![]()
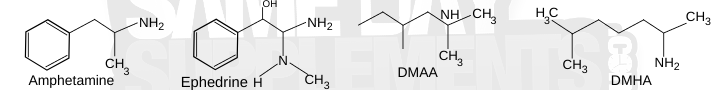
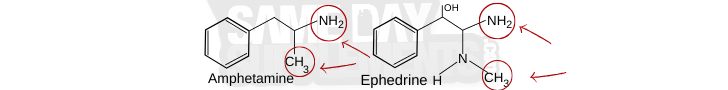
Similar To Ephedra Pills:
Ephedrine isn’t the only stimulant people talk about. Over the years, other compounds like DMAA, DMHA, and even amphetamines have been compared to it because they work in similar ways on the central nervous system (CNS). Here’s a breakdown of how they compare:
DMAA VS Ephedrine:
Like ephedrine, DMAA was a popular stimulant no longer in dietary supplements. Both ephedrine and DMAA are central nervous system (CNS) stimulants and share some structural similarities. However, DMAA toxicity is described as being greater than ephedrine (but less than amphetamine). (23) They have similar uses because of their similarities in structure. In fact, they share the same medicinal uses as a nasal decongestant. However, these stimulants are both vasoconstricting substances. (24)
DMAA also shares structural similarities with adrenaline. Because of this, its mechanism may be adrenaline mimetic, inducing the same effects as adrenaline.† Unfortunately, direct studies on the pharmacokinetics of DMAA metabolism do not exist.
Takeaway: DMAA and ephedrine produced overlapping “wakefulness + metabolism-boosting” effects, but DMAA tended to hit harder, and safety concerns eventually pushed it out of supplements.
DMHA VS Ephedrine:
Similarly, DMHA was used as a nasal decongestant and is also vasoconstricting. The most significant difference between DMHA and ephedrine is that DMHA is legal! But structurally, there are more similarities between DMAA and DMHA than with ephedrine. So how does DMHA work?
Due to it being a methyl group on the alpha carbon, it should have a half-life of about 9-11 hours. And it should act as a monoamine-releasing agent (MRA) of catecholamines like DMAA. This includes dopamine and norepinephrine.
Then DMHA binds to the trace amine-associated receptor 1. This will temporarily prevent the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine into the presynaptic nerve. By doing this, these catecholamines remain active in your body for longer. This contributes to the euphoric and wakeful feelings we get from ingredients like this. (25)
Amphetamine VS Ephedrine:
Amphetamine, similarly to ephedrine, releases stores of norepinephrine and dopamine. However, amphetamine can also release stores of serotonin. They also prevent dopamine/norepinephrine transporters from recycling those neurotransmitters, prolonging their effects. (26)
Takeaway: While ephedrine is strong, amphetamines are far more potent and risk-laden, which is why they are tightly controlled substances and not comparable in supplement safety.
![]()
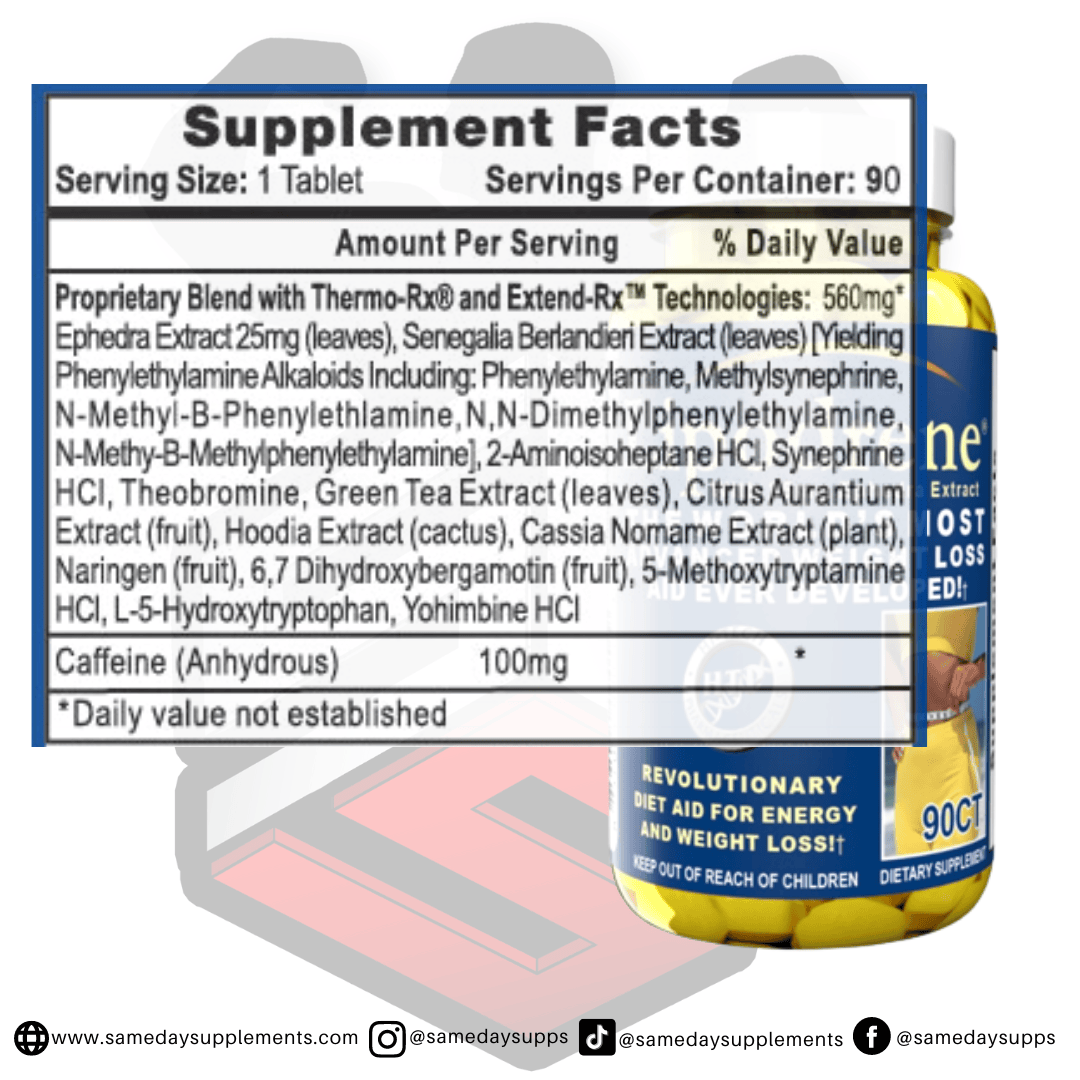
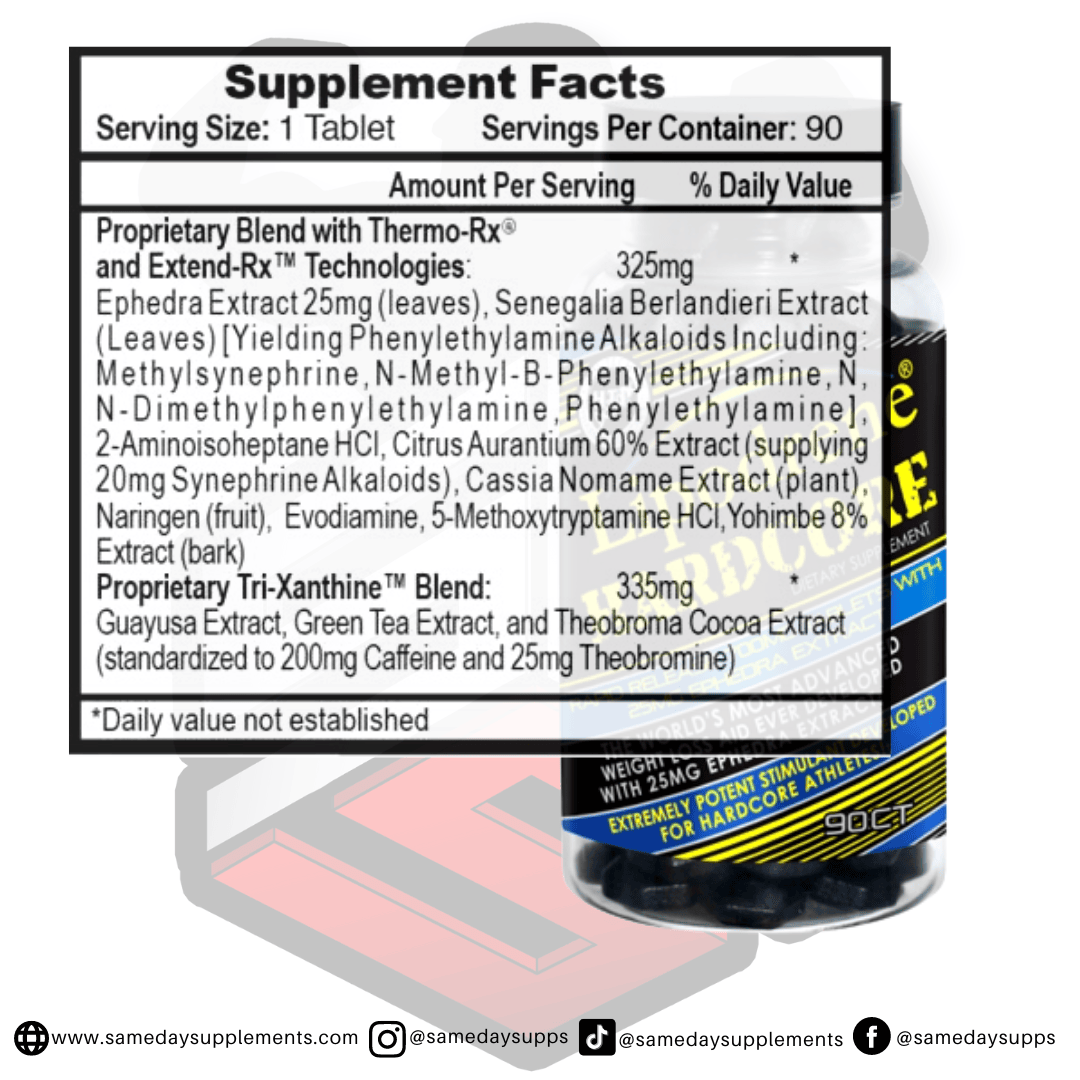
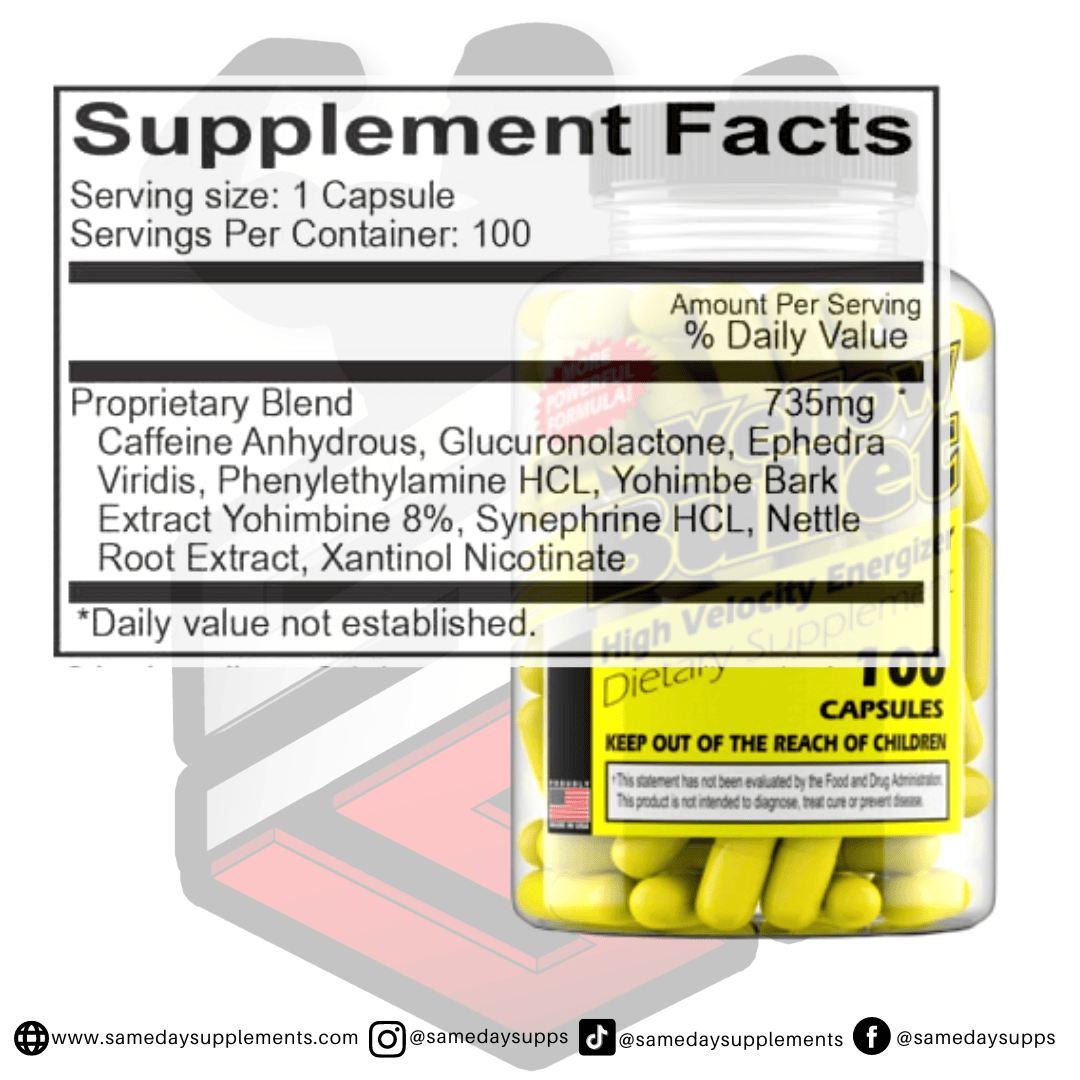
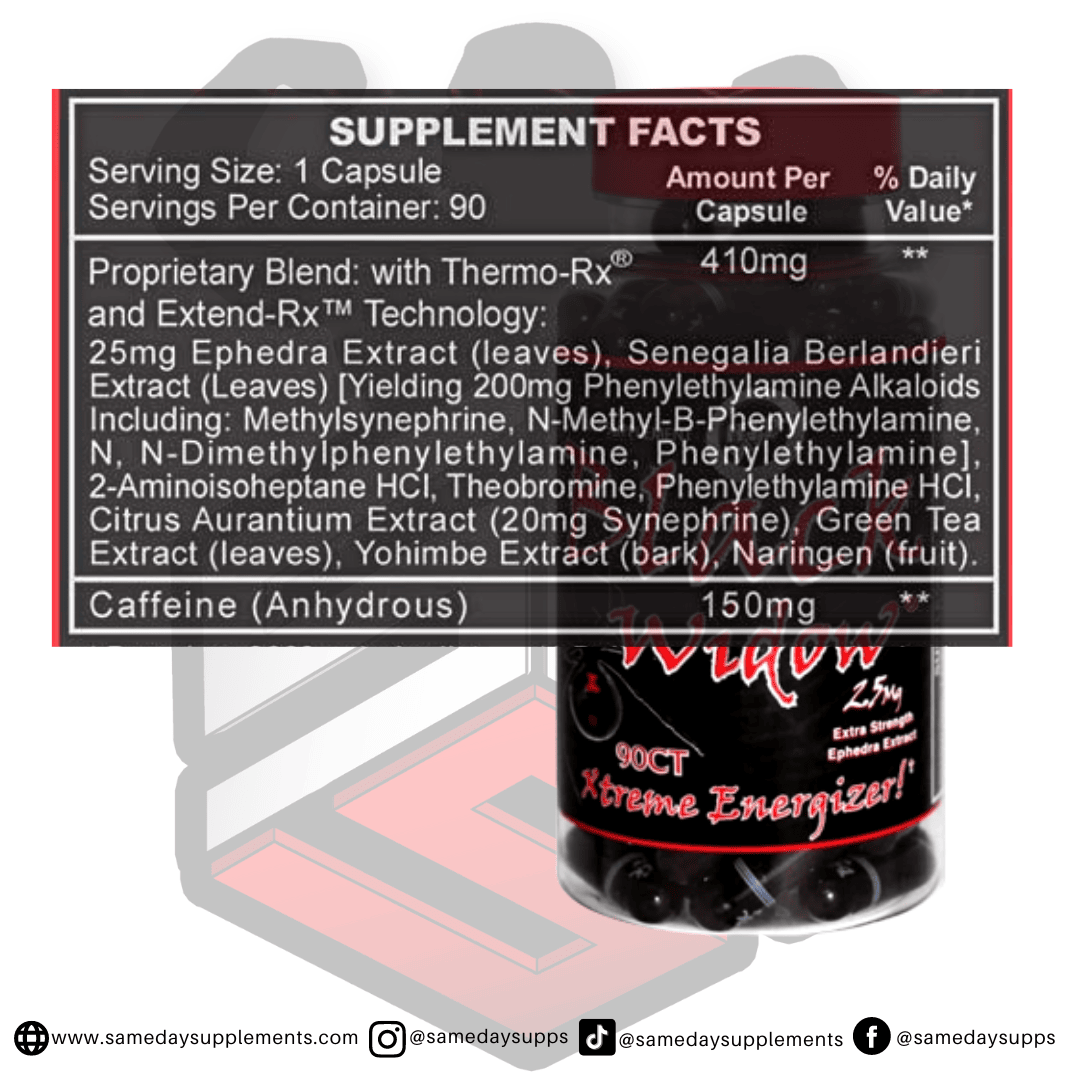
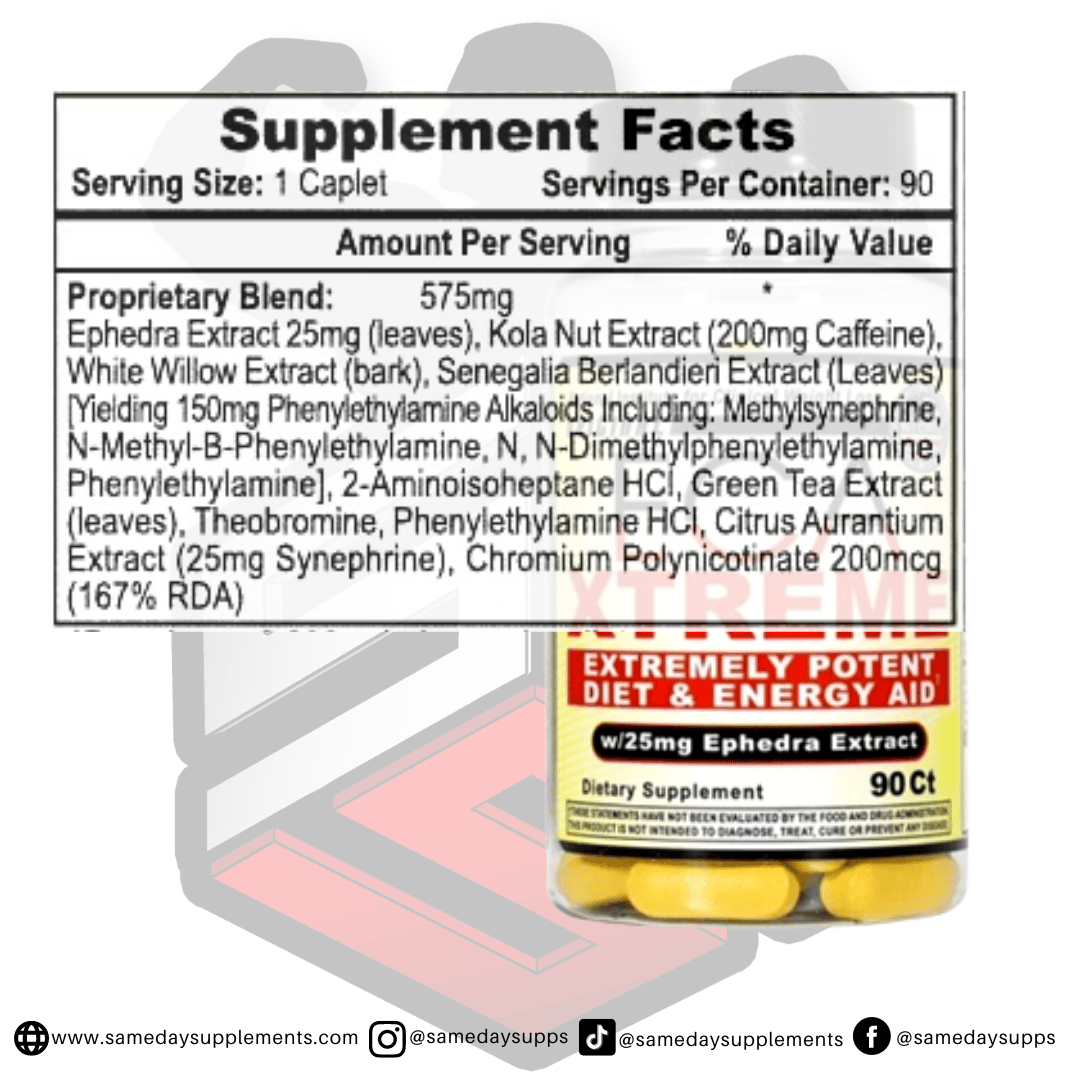
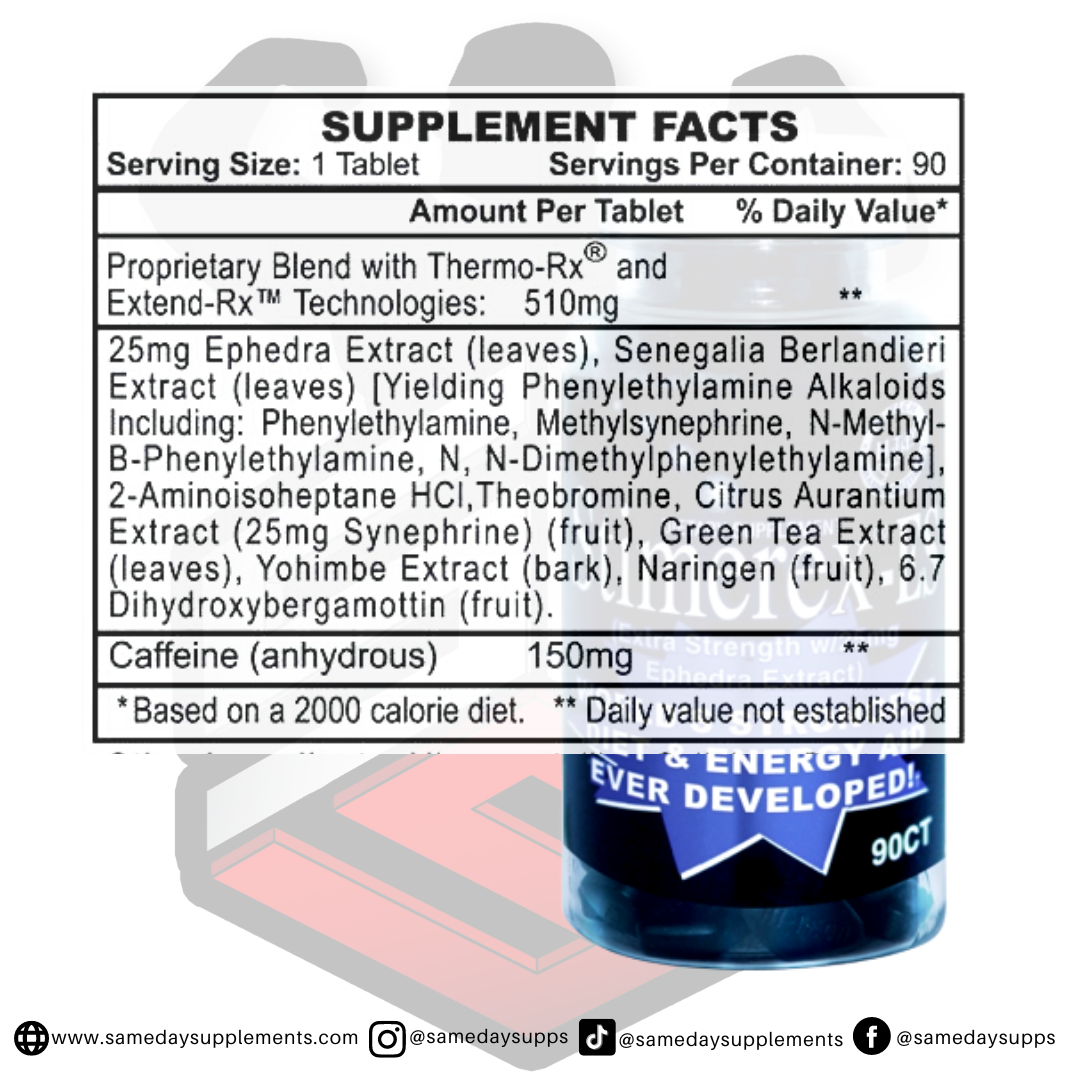
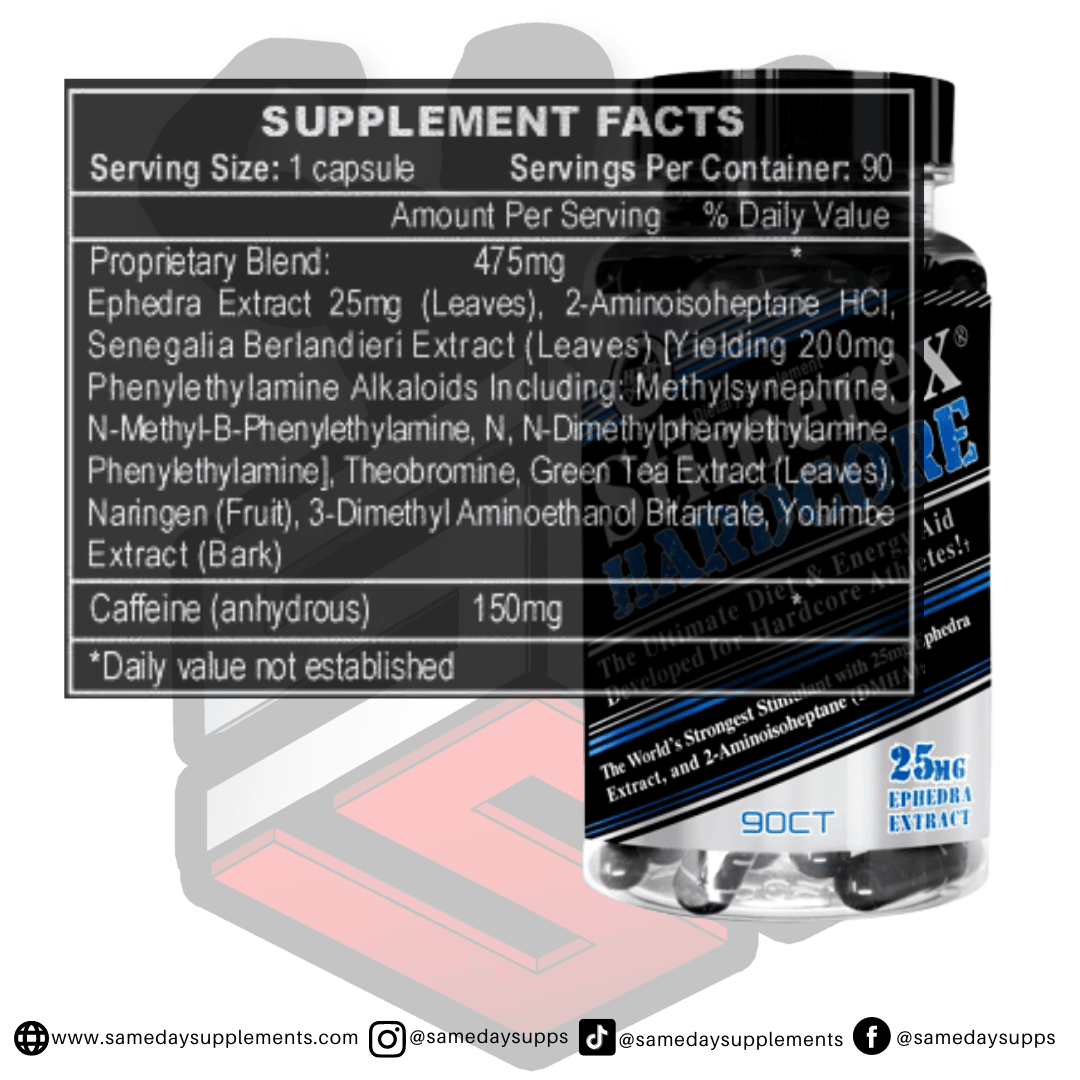
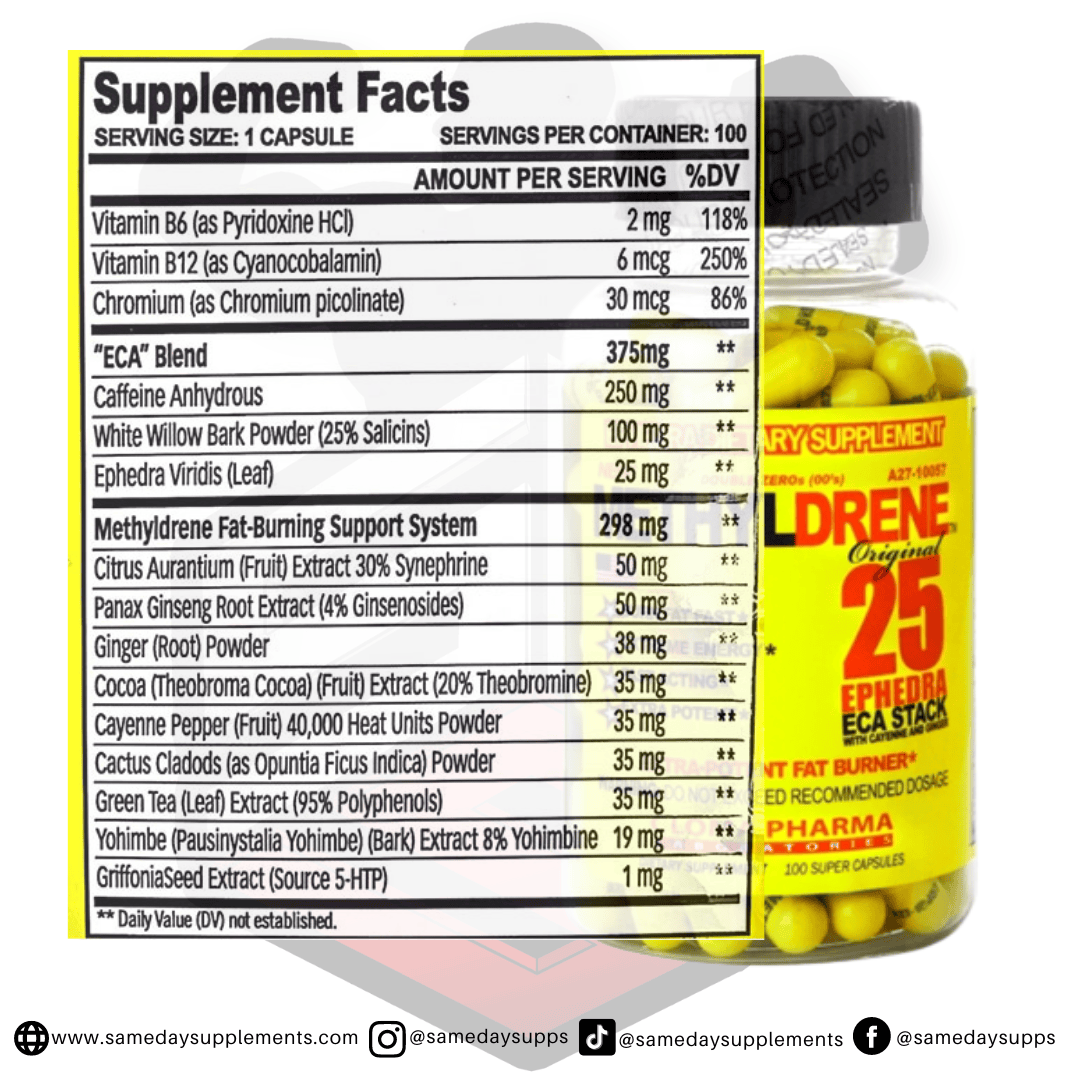
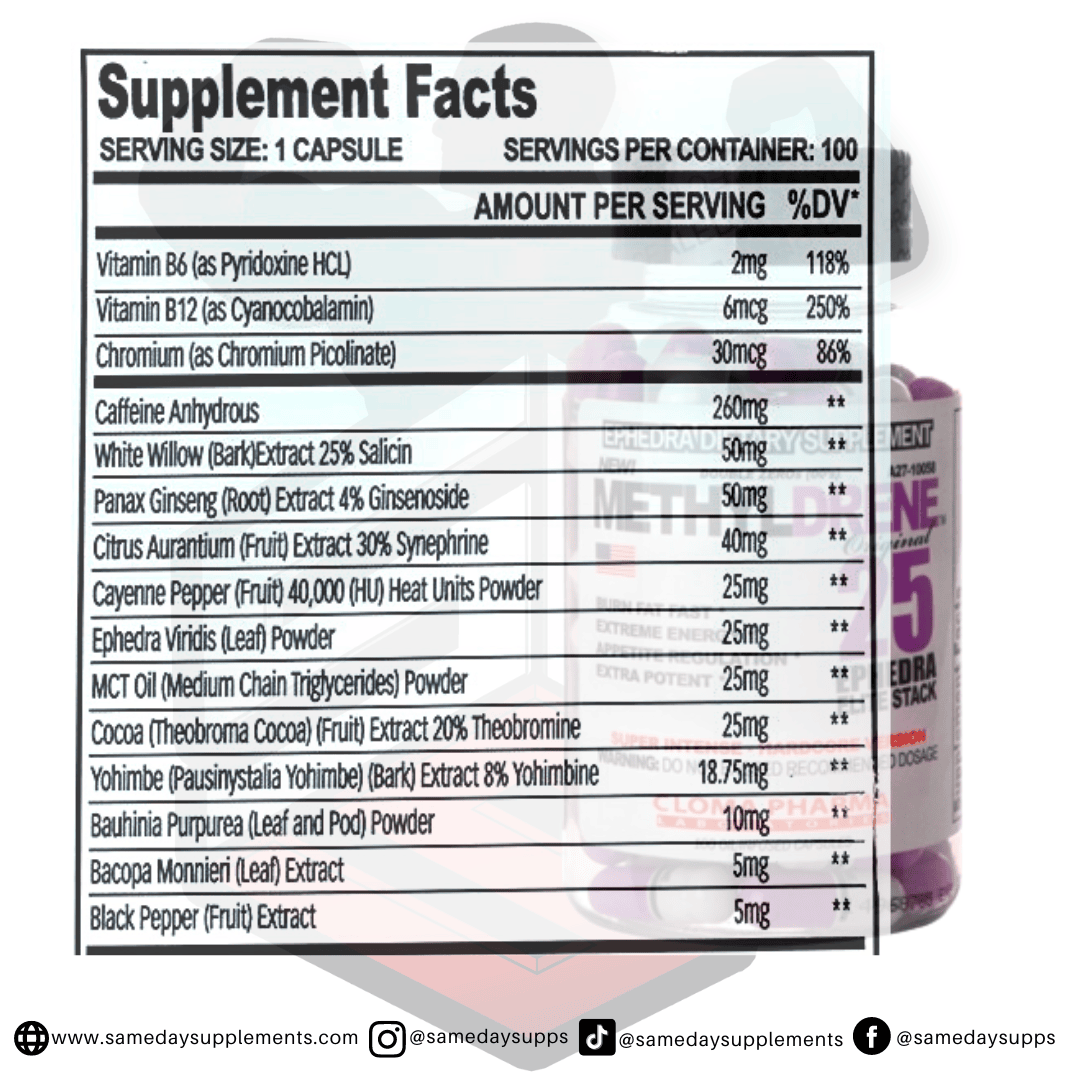
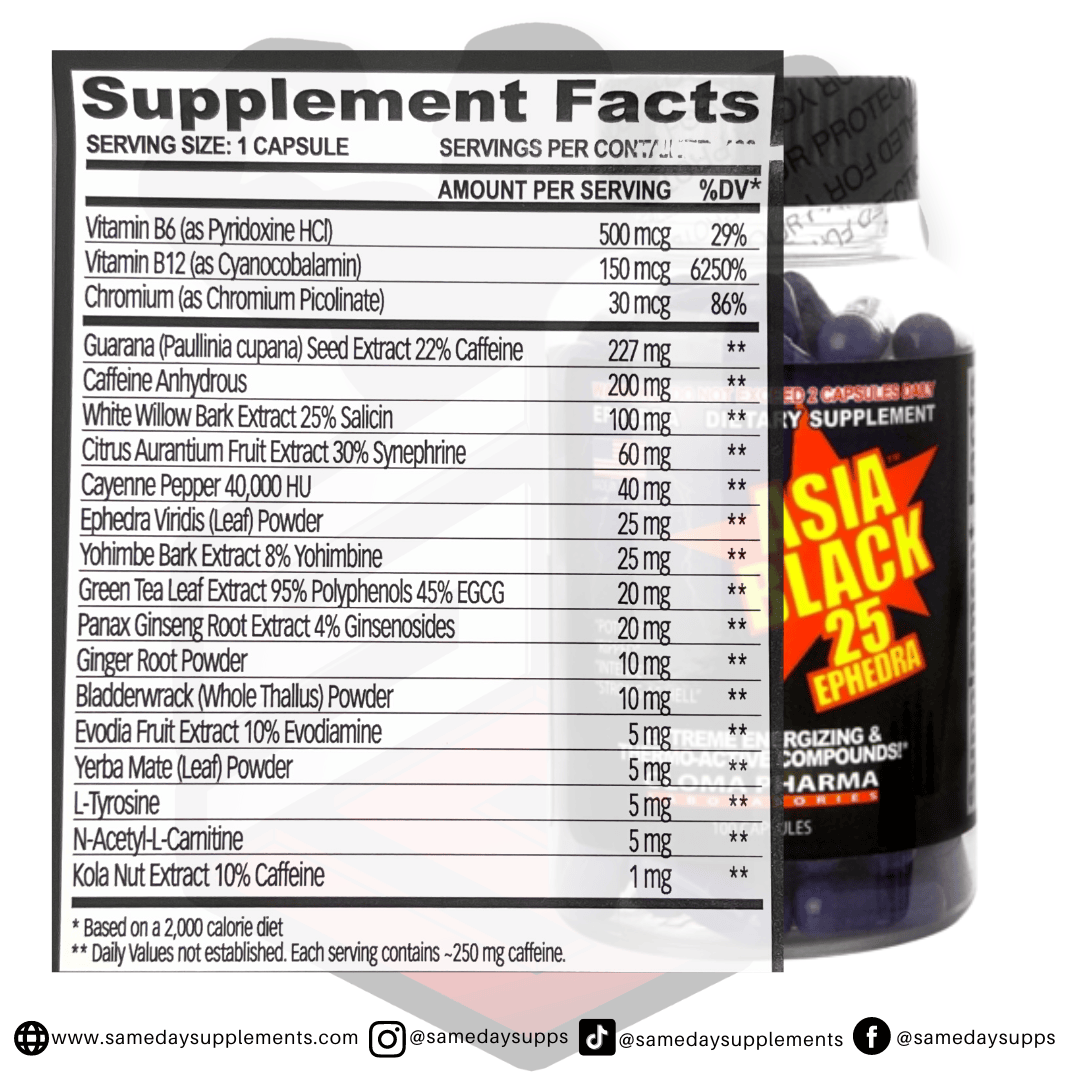
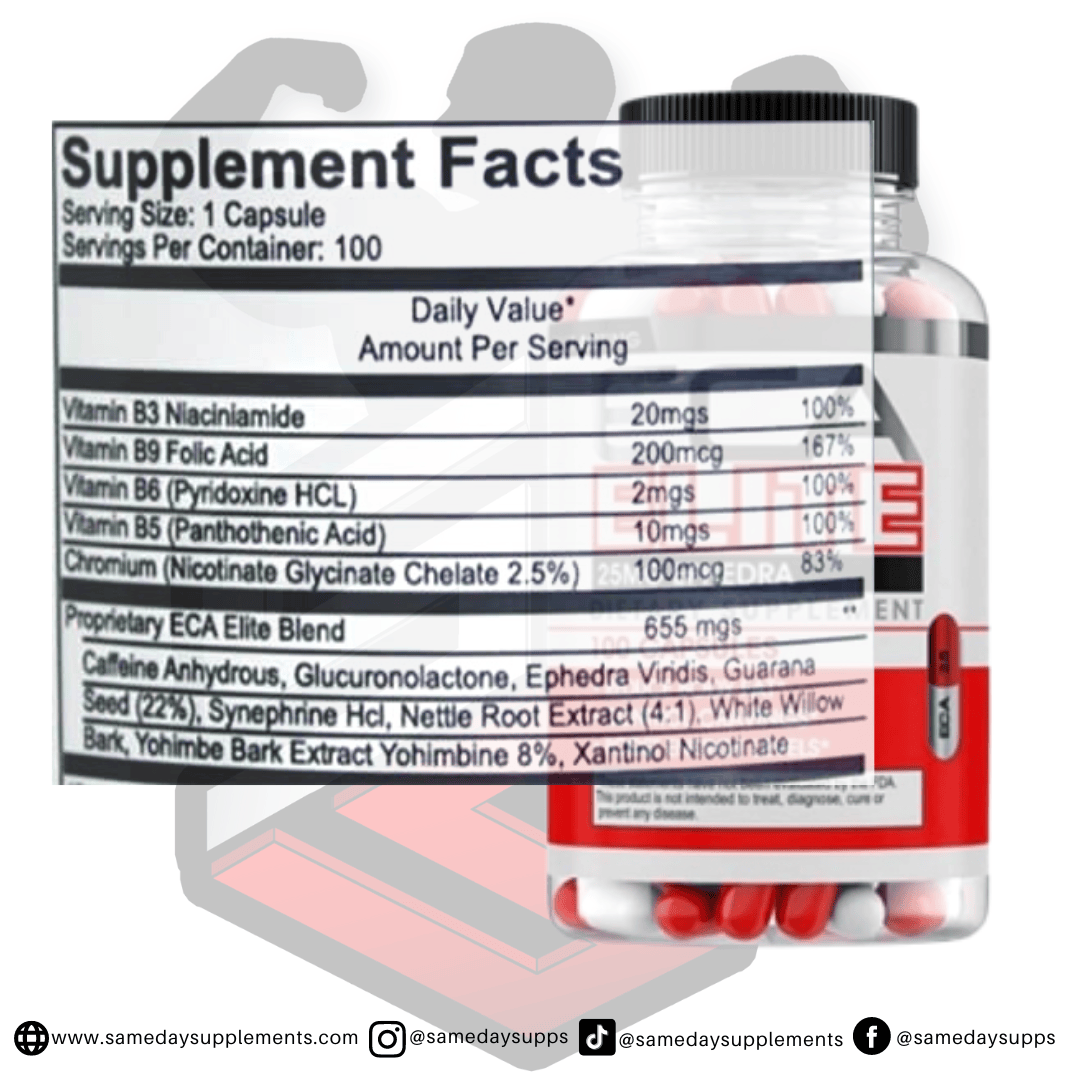
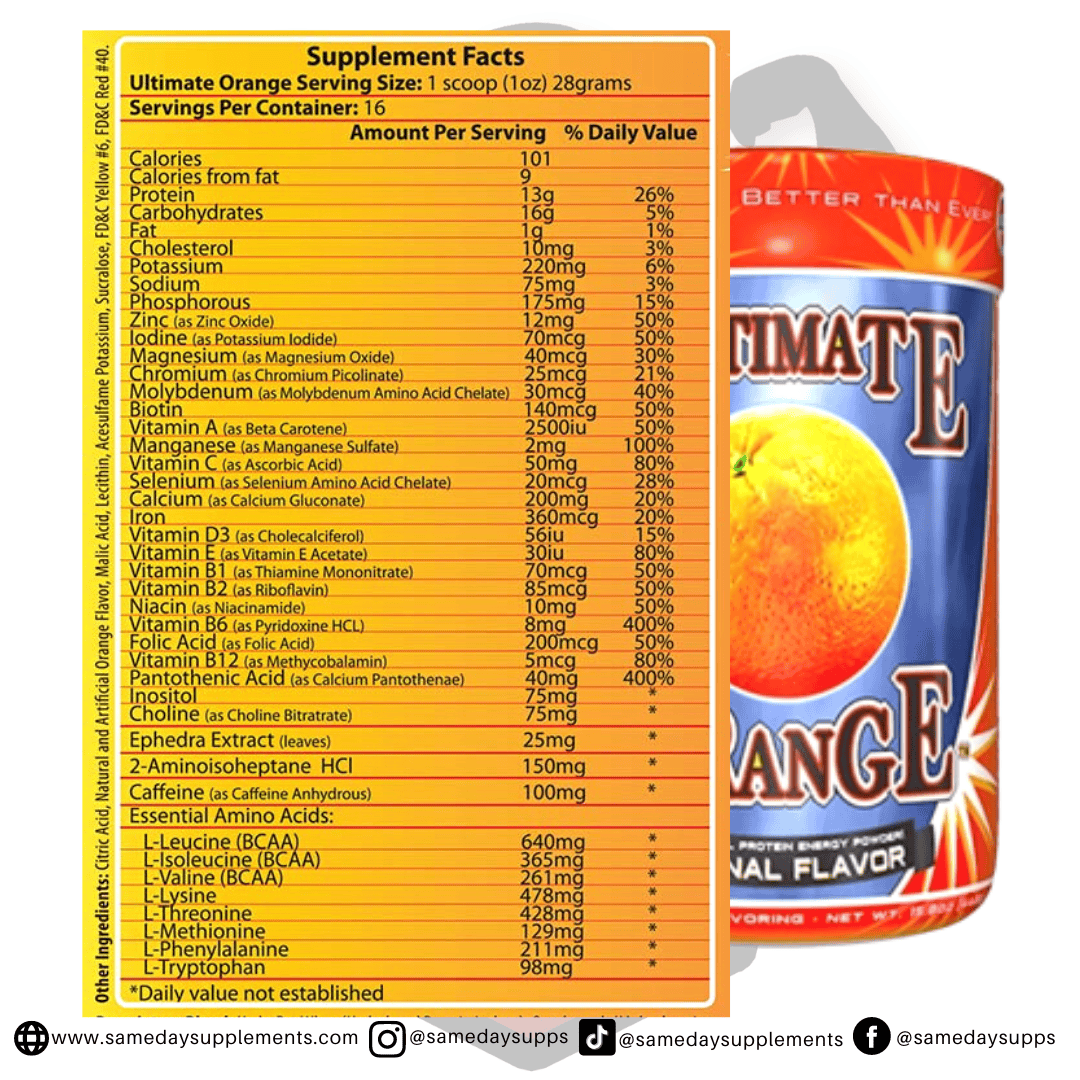
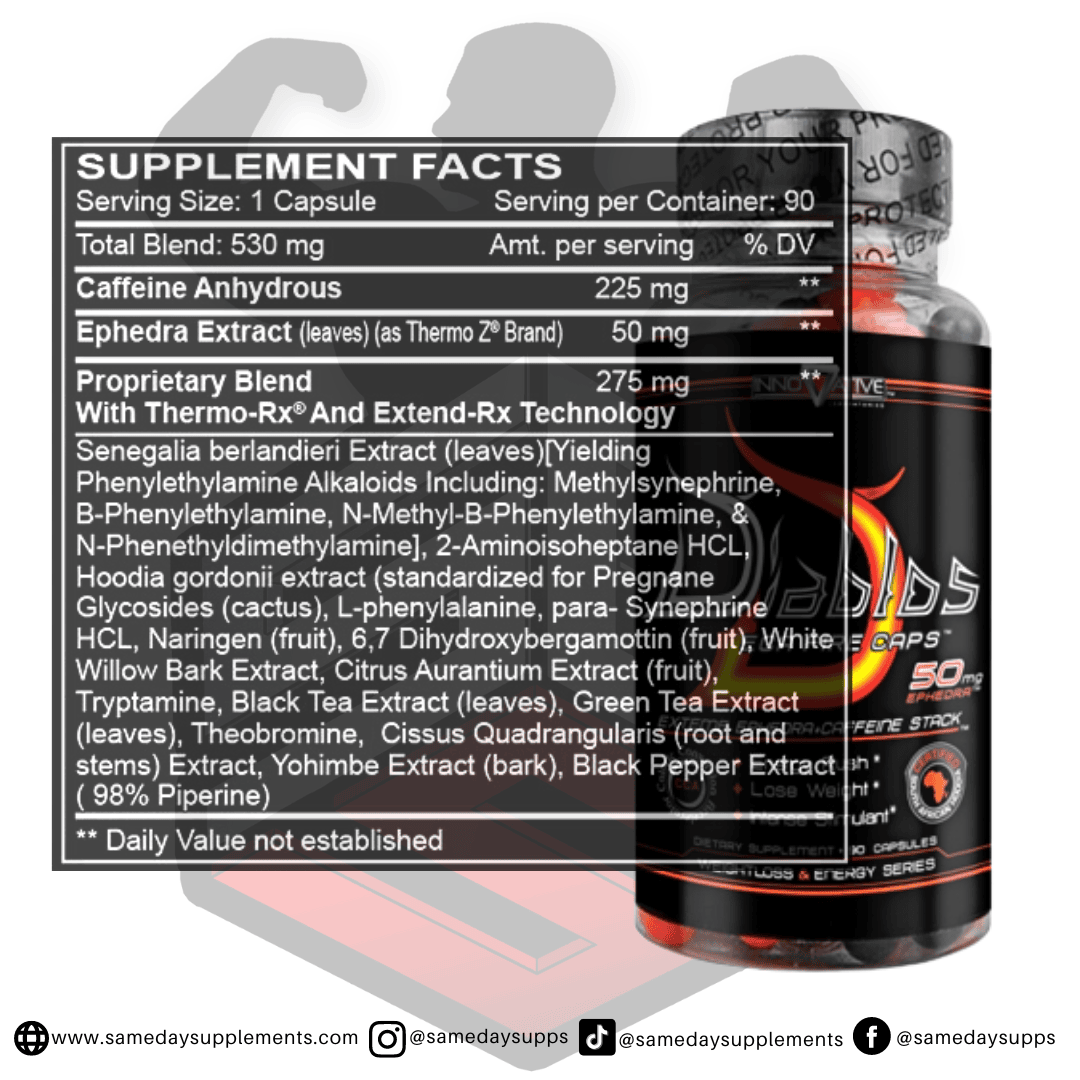
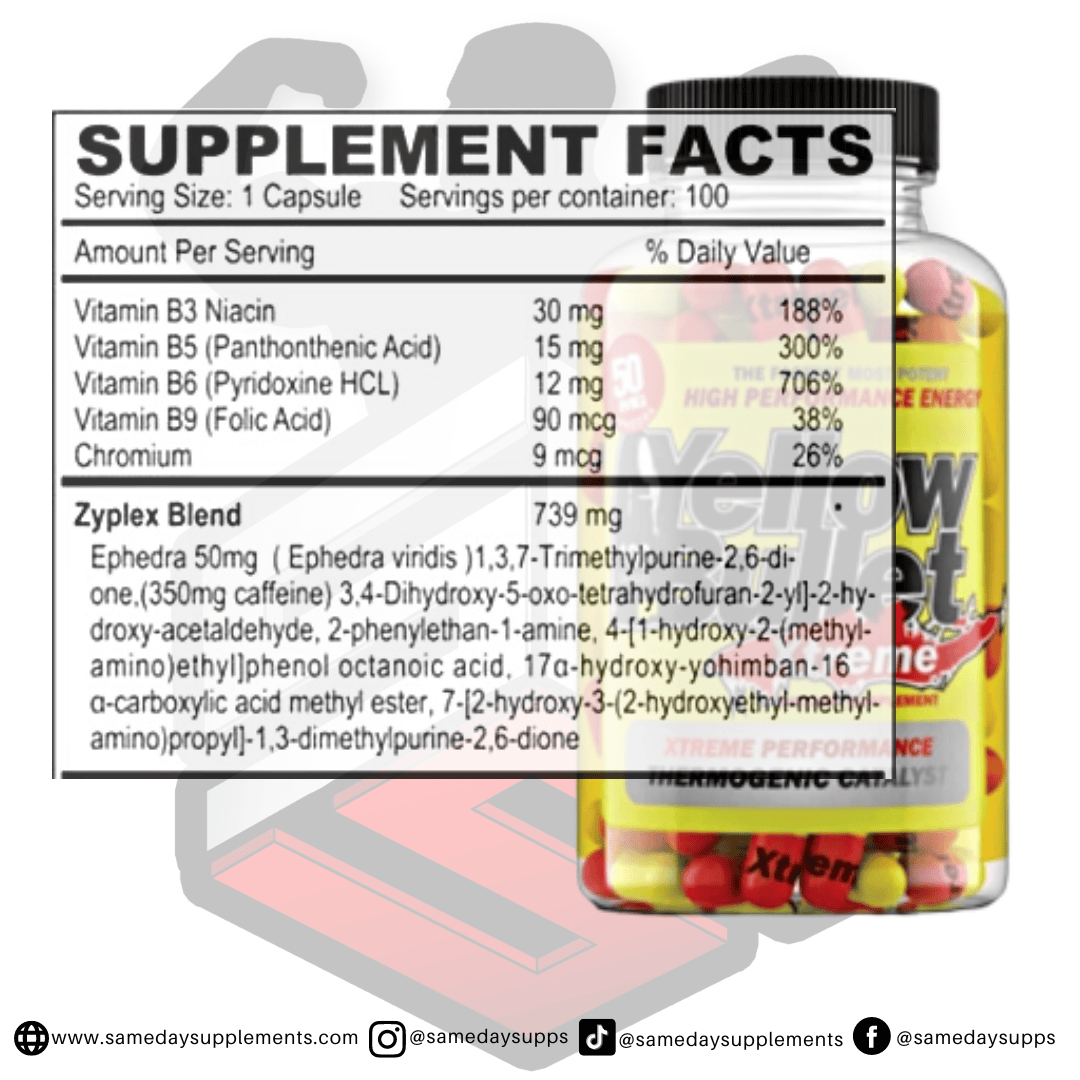
Popular Ephedra Pills Products
Ephedra is a common component in many fat burners. Browse top options by ephedra content, read real customer quotes, and click through for full details.
![]()
Where to Buy Ephedra Fat Burners
You can find all the Innovative Labs fat burners right here at SameDaySupplements.com!
Looking to take your results even further? Check out our Weight Loss Stacks, featuring your choice of fat burner paired with CLA 1000 and Carnislim for a complete fat-loss combo.†
🚚 All orders ship same day (M–F before 3 PM EST)
✅ Trusted U.S. retailer with verified reviews
💥 Stack deals available for even more savings
![]()
Wrapping Up!
This marks the end of our ephedra VS ephedrine post! To help wrap things up, if you’re dabbling in fat burners and want to try one of the ephedra pills, we recommend sticking within the 25mg range. However, if you’re an experienced user and looking for the max, Hellfire or EPH 100 is the fat burner for you!
Thank you for reading! And as always, if there’s something unclear, you have another question, or you have another idea for a blog, email us!
Are you looking for more to read? Check out some of our other blogs!
- Tricaprin, Caprylic Acid, and MCT Oil Supplements
- The Science Behind Minoxidil
- Is Crack Pre Workout Safe to Use?
- Lipodrene VS Lipodrene (What to know)
![]()
Warnings And Side Effects:
- Not for anyone under 18. Do not use if pregnant or nursing.
- Contains stimulants—do not combine with caffeine, synephrine, or similar ingredients from coffee, tea, soda, other supplements, or medications.
- May raise blood pressure and interfere with prescription drugs. Always consult your doctor before use.
- Not recommended for use longer than 8 weeks.
Consult a physician first if you:
- Take medications (such as MAOIs, aspirin, antidepressants, NSAIDs, or stimulant products)
- Have medical conditions (including heart, liver, kidney, or thyroid disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, psychiatric or seizure disorders, arrhythmia, enlarged prostate, glaucoma, or history of stroke/headaches)
- Stop use immediately if you experience a rapid heartbeat, dizziness, severe headache, or shortness of breath. Discontinue at least 2 weeks before surgery.
- Overdosing or exceeding the recommended serving may cause serious health risks, including a heart attack or stroke. Avoid alcohol while using this product.
This product may also contain ingredients banned by some sports organizations and could trigger a false positive on drug tests—check with your organization or physician before use.
![]()
Disclaimer:
†Please note the intention of the information provided is for reference only. Furthermore, we are in no way providing medical advice or instruction. Instead, the information provided in this guide/blog utilizes anecdotal information and available studies/reviews. While we aim to maintain and display accurate information, we can’t guarantee it represents the latest product formulation or information. Therefore, please visit the manufacturer’s website if you have any concerns. Also, the information above does not represent our views here at Same Day Supplements. Instead, these are the manufacturers’ and users’ views and information. Additionally, the Food and Drug Administration has not evaluated these statements. Finally, these products aim not to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent disease or illness.